When she was introduced in 1983, the Rob Roy 23 captured all the popularity that Ron Johnson, her Florida builder, could handle. Marine Concepts, Johnson’s small custom shop, built and sold 85 in less than 10 years. The Rob Roy was then retired in favor of Johnson’s Sea Pearls (Sea Pearl 21, Sea Pearl Tri-21, and Sea Pearl 28.)

Now the little cruiser is back, with the first new ones being launched in 1998, for “about what the last one we built cost—around $26,000 complete,” Johnson said when we talked to him in late 1997.
We wondered what sort of 23-footer could command that price. In 1983, it was the only trailerable canoe-stern yawl in town. Its appeal, however, goes beyond novelty. This is a boat with character: She looks salty; sails well with working sails alone; and she provides accommodations for two. Simplicity, from a space-saving centerboard to a “hardened” kick-up rudder, from an unstayed mizzen mast to a tabernacle-mounted mainmast, is a watchword. The Rob Roy can be launched at a ramp and is easily beached due to its 1′ 7″ draft with the board up. Owners have cruised her for weeks at a time and routinely cross the Gulf Stream and other formidable chunks of open water.
On the other hand, sitting headroom and moderate beam limit the space below, even for a pocket cruiser. There’s no shortage of boats in her size range with bigger cockpits. The canoe stern steals space, and an outboard well has its pros and cons.
To answer the question of her popularity, one must look deeper. As is our practice at Practica Sailor, we asked the owners about trailering ease, outfitting, durability and her woeful forays into PHRF racing.
The Design
As we learned, the Rob Roy not only created a minor buying frenzy when she appeared, it won a group of vocal and committed owners.
“This is THE boat,” said one owner. “I don’t want anything bigger and I can’t imagine anything better.”
Designed by Ted Brewer, the Rob Roy was inspired by the turn-of-the-century adventures of John MacGregor. His little 20-foot canoe yawl was so portable that he carted her aboard trains, yet she was tough enough to let him leave the protection of the River Humber and explore the British Isles from end to end. MacGregor not only named his freedom-giving yawl after his famous ancestor, he also inspired the Humber Yawl Society of which designer Ted Brewer is a member.
“I admire those boats and their voyages,” Brewer told us. “Lord Baden-Powell, who started the Boy Scouts, was president of the group early on. The Humber yawls were all canoe-sterned with plumb ends. They got bigger than the original Rob Roy, up to 24 or 26 feet. They had gaff or gunter rigs. My Rob Roy design owes a lot to their spirit but not a great deal to their specifics.”
Brewer’s career began in the late 1950’s. He’s worked on both the East Coast and West Coast (he now practices in Lyman, Washington), and his designs range from race boats such as Storm and American Eagle to cruising boats like the Panoceanic 46 and Quickstep 24.
“With the Rob Roy,” he said, “I was trying to keep the rig manageable and still have her sail well, to give her enough beam to stand on her feet but not so much that she’d be slow, to stretch out her design waterline, build in a lot of form stability, and still have her look handsome. Design is always a series of tradeoffs. In a boat of this size that’s especially true. The time that I spent in the navy sailing 26-foot open whale boats showed up in the design, too. Early in the design process I decided that I very much wanted one of these boats for myself. That tends to make you pay a particular kind of attention.”
What he came up with is hardly your average boat, but she is nevertheless a boat that addresses the needs of the average sailor. The 6′ 6″ cockpit seats are straight and comfortable enough to take a bit of the curse off having only two berths below, but the Rob Roy 23 is essentially geared to support two adults, and only two. That decision had its greatest impact on the interior arrangement, but other aspects of the design—like cockpit size, design displacement, and sail plan—reflect it, too.
One owner said, “I would have to rate the design as first rate, especially the double-ended look, the centerboard raising into the keel, the deep cockpit, the sail leads and hardware arrangements.”
Construction
The original Rob Roys were built of fiberglass with balsa coring in hull and deck. Johnson now builds his standard Sea Pearls and his new Rob Roy with foam cores. He says that the new foams have improved resistance to water migration and superior temperature and noise insulation.
“But,” he said, “we’re essentially a custom shop and the customer can get whatever type of core he wants.” One owner reported that the core beneath the mast step was squashed when he tightened his rig. “That sort of thing should never happen, but it did,” Johnson admitted. “We fixed it, but whether the core is foam or balsa a high-compression spot like that should always be solid glass, and in the Rob Roy, it is.” Despite that experience (or maybe because of Johnson’s handling of the problem), the owner in question rates the construction and finish of his Rob Roy as “excellent” and added, “I do not know of trailerable boat that I’d rather have.”
“We use the best gelcoats,” Johnson said. “We’ve found antique colors that don’t absorb heat or radiate much glare. ‘White sails’ is our standard deck color or for an additional $280 you can have a two-tone deck where the non-skid portions are done in ‘Whalebone’.” Hull colors are a no-cost option. Behind the gelcoat comes a barrier coat of vinylester resin. We use Stitchmat (a fabric made by stitching layers of mat together on the bias) to prevent print through. The remaining hand-laid rovings that make up the laminate are wetted out with polyester resin. The Rob Roy has extra layers of rovings in the keel and trailer impact areas.”
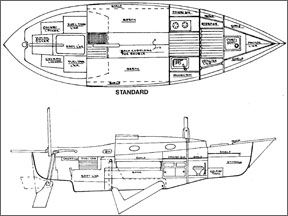
There is a small interior glass unit, very similar to what, in larger form, might be called an interior pan. It forms part of the sole and locates the bulkheads and furniture. It’s not structural. The bulkheads and furniture are double-tabbed to the hull. The bulkheads and furniture are faced with teak. Trim is solid teak. The archway in the central bulkhead is ringed with teak and is supported by solid pieces of teak that reach to the keel.
“You couldn’t build boats like the Rob Roy anymore,” one owner said. “The wood and the finish below would make it too expensive.”
“Marine Concepts provides excellent quality in basic construction. No problems with blisters after 12 years,” reported another.
One construction feature, though, that has been changed with the new Rob Roy is the make-up of both the centerboard and the rudderblade. Said Johnson, “The old centerboard was an aluminum plate and the old rudder was a sandwich with an aluminum plate in the middle. Boats that were kept in the water experienced electrolytic activity. due to the stainless steel weldment at the bottom of the rudder shaft. Owners can and should protect those blades with zincs if they keep the boat at the dock or mooring instead of on a trailer.”
The original board was hung from a pivot pin assembly that fits in the forward end of the centerboard slot but remains external to the hull so it won’t cause leaks but will allow the board to be removed for repair or even cleaning. The original board was shaped like an “L” lying on its back. The foot (or short side) of the “L” is housed in an abbreviated trunk, but forward of the companionway the remainder (or long side) of the board is housed entirely below the sole. You control the board via a simple, one-part tackle from its uppermost after- corner. The configuration leaves the saloon free from an obtrusive trunk.
The kick-up rudder connects to an angled stainless shaft. The shaft works well without bearings and has proven to be durable. The point where the blade joins it, however, seems thin and vulnerable. The joint is (just) protected by the keel in front of it. Neither Johnson nor Brewer has heard of a rudder being damaged. It appears as though a grounding in reverse or even maximum rudder torque might change that box score, but then steering loads on a moderately rigged 23-footer aren’t that extreme.
The blades on the new boat are made of glass. The new board probably will have a foil-shape.
The hull/deck joint has changed. The first 85 boats were built with an inward-turned flange molded into the hull. Johnson has now gone to an outward-turned flange “because it’s easier to finish off and make leak-proof.” He will still use 3M 5200 and mechanical fasteners to make the joint and will still cover it with a solid caprail. “The Rob Roy record on deck leaks is excellent,” he said, and the owners surveyed agree.
One owner had a persistent problem with a companionway leak. “It appears, after much back and forth, that there was no bedding in the original joint,” Johnson told us. “We fixed the problem but it cost me time and money to get it sorted out.”
During Rob Roy’s life, her bowsprit and boomkin have usually been 2″ x 6″ and 2″x 4″ balks of teak respectively. “I’ve built beefier ones for people that wanted them,” Johnson said, “but I never quite saw why.” Johnson remembers. Several owners expressed the wish for a detachable bow sprit to make trailering simpler and to reduce her “marina length” from a length overall of 28′ 8″ to her on deck length of 22′ 8″. “I used to do that,” Johnson recalled. “We’ve simplified by making the spars permanent, but if an owner wanted removable ones it’s easy to do.”
The Rob Roy 23 carries 900 lbs. of ballast (including the weight of the centerboard). The shallow keel is filled on either side of the centerboard trunk with small chunks of lead held in place with casting resin. A small sump is left in the after end of the keel.
Interior
“I must admit that I designed the Rob Roy accommodations for myself,” Brewer said.
The head is forward and benefits in terms of room and privacy. It’s not ideal for use at sea, however. An optional plan moves the head to port and inserts a child’s berth to starboard. Aft of the single bulkhead is the galley—stove to port, sink to starboard. Opening portlights provide ventilation. The saloon consists of settee berths that extend under the cockpit.
They are low enough and the house sides are wide enough to make for comfortable, “no-slouch” seating throughout. The shelves outboard of the berths are convenient but minimal and would benefit from taller fiddles. Four cockpit lockers and a raft compartment below the cockpit sole make on-deck stowage one of the boat’s strongest suits. Below, the majority of stowage is forward.
The centerboard trunk is capped with solid teak and extends just a foot into the interior from the companionway. “One or two can live aboard for one or two weeks” was the refrain from owners. “Having the galley forward took some getting used to, but now I like it,” said one.
Freshwater capacity is 14.5 gallons and there is a holding tank forward.
The berths convert, via an insert, into a platform double. “The boat is unparalleled for two—good bed, good head, great lighting,” said an owner after cruising the Rob Roy (his seventh boat) for five years.
Trailering
Marine Concepts offers a trailer with the Rob Roy that costs $2,850. It comes with dual axles and is made of galvanized steel. It has 14″ wheels, surge brakes, bearing buddies, a tongue jack, and a spare tire. One owner figured his towing weight to be “about 4,200 lbs.” Over the years, some owners have mentioned trailer problems, to which Johnson said that he has changed vendors.

The standard trailer comes with custom-made beds spaced and angled to suit the boat. Given the boat’s draft, the trailer must be at least partially submerged—weight placement is critical to an easy retrieval as well as a comfortable tow. No owners have yet nominated trailering as a highlight of their Rob Roy experience.
Performance
The Rob Roy 23 is built to carry an 8-hp. Honda 4-stroke outboard in a well. (Some boats have been modified to accept a saildrive, an inboard powerhead, either gas or diesel, on a fixed vertical drive unit.) The outboard remains fixed in the well when the boat is under sail, so propeller drag is greater than if it were on a bracket or retractable. The convenience of having power on demand and the efficiency of a propeller that is mounted where it will provide good thrust even while the boat is pitching in head seas somewhat offsets the loss in sailing performance. The motor is mounted just aft of the keel which helps to diminish its parasitic drag under sail but presents the possibility of cavitation from running in aerated water under some powering conditions. The exhaust ports built into the well have proven satisfactory but many owners have increased the standard air intake (by replacing the solid well cover with a grating or adding cowl vents or cutting holes for ducts in the coaming) to relieve the tendency of the outboard to starve under load.
There is room for two 6-gallon fuel tanks in cockpit lockers.
Yawls are a rarity on the new boat market but the Rob Roy isn’t totally alone. Garry Hoyt recently introduced the Alerion Express 36 with a yawl rig. By adding a mizzen, Brewer increased the Rob Roy’s sail plan to 255 square feet. That results in a snappy sail area/displacement ratio of 20.8. Perhaps that is the root of a PHRF rating for the boat that has caused the few owners who have raced her to bemoan the experience. That sail area works fine on a reach, but upwind any mizzen, especially one set as close to the main as the Rob Roy’s, suffers from mainsail backwind. Downwind the mizzen works okay but it steals air from the main. It’s not surprising that racing yawls went out with black and white TV.
Balance, versatility, and small, easily managed sails are the virtues of the yawl rig, and the Rob Roy enjoys them all. On the flip side, this sail plan prevents the boat from accelerating as fast or developing as much horsepower as she might with the same area of sail divided into two larger units—or even lumped into one. Brewer offset this disadvantage in a number of ways. He kept the waterline beam on the slim side, cut back the forefoot, and faired the waterlines to make the hull very easily driven. The Rob Roy is a relatively light boat, even with two adults aboard. She has a minimum of wetted surface, especially with the board up. These factors make her a very respectable light air performer.
Sailing in a Buzzard’s Bay sou’wester cycling from 16 to 20 knots we saw the Rob Roy at her best. With three large men sitting to weather she cut through the chop heading upwind without dipping her rail or spilling wind from her sails. Dousing the mizzen helped her stand a bit straighter, but when we set it again it was hard to tell what difference it made. We rolled it around its spar and left it furled. Not as close-winded as sharper, deeper boats might be in waves, she picked up markedly when we cracked her off to 38° to 40°. We tacked consistently through 90°. It’s true that when you reef the center of effort moves forward and we found it nice to balance the boat by re-setting the mizzen. Across the wind we tried jib and mizzen alone and were rewarded with bursts approaching its 6- knot hull speed. Even with the wind near the top of its range we handled all sails by hand and found no need to crank on the winches. One owner described his boat as “extremely seaworthy,” noting that “She’ll lay over but she picks up stability as she goes.”
Hard bilges give the boat good initial stability. The flared hull, efficiently placed ballast and moderate sail plan all make her progressively stiffer as she heels. She’s a pleasing boat to sail in a breeze—responsive yet resistant. The helm is light and by playing with the centerboard and mizzen you can get the boat to steer herself on most points of sail. She’s dry for a boat of this size and has a predictable and deliberate motion even in a chop. There isn’t much room for that third person in the cockpit, however.
Conclusions
The Rob Roy has an appealing look all her own and some features that make good sense in a pocket cruiser. Limited accommodations means maximum space for two persons and keeps both stowage and performance capabilities from being overloaded. Her small cockpit is fine in a seaway and adequate for two but cramps her versatility as a daysailer. The yawl rig is simple and provides a built-in riding sail and virtual steer-by-the-sails control. She doesn’t have enough working sail area to be quick in light or even moderate air, but she can be sailed without winches and she handles heavy weather very well.
Marine Concepts works hard to keep its owners happy, but don’t look to Ron Johnson for much innovation. He seems almost the antithesis of Stan Spitzer, whose Rhodes 22 we reviewed in the August 1 issue. “He hates gadgets,” one owner said of Johnson. He builds conservative boats and has shown that he stands behind them. The Rob Roy’s design wrinkles, construction, and outfitting have all helped her become one of the few “offshore trailerables” available.
Price is a bit more than what Johnson predicted: $28,000, which includes sails, portable toilet and 8-hp. Honda four-stroke outboard. For those interested in a used model, the 1983, which originally sold for $16,000, is worth just $5,650-$6,500 today. A 1988 model, according to the BUC Research Used BoatPrice Guide, goes for $11,600-$13,200.











where can we get detailed schematics of Rob Roy Yawl ?
Yes, I’ve looked everywhere online for some kind of schematic of my 1987 Rob Roy 23’. I even tried to contact Ted Brewer the designer, his web page says you can get owner sets for production boats. The phone number isn’t good and email is full.
Yes, I’ve looked everywhere online for some kind of schematic of my 1987 Rob Roy 23’. I even tried to contact Ted Brewer the designer, his web page says you can get owner sets for production boats. The phone number isn’t good and email is full.
I may be able to help. I bought a 1987 Rob Roy 23 last August. It’s now in winter storage, but I’ve been looking thru a box of paper work that came with the boat. It appears to be a complete set of plans & specifications.
Hey Brad, sorry i didnt get back with you sooner. I felt like this wouldnot be answeredi guess. I just subscribed to practical sailor and found your response. So sorry to hear Ted Brewer passed. Thank you for that information. Would love to get copy of Rob Roy schematic! Do you raise your mast by hand or use mechanisms. Everyone says we should be able to just walk the mast up usinf rolling furler jib as leverage. It seems risky to me?
Btw… Ted Brewer passed away last year. There was a nice tribute to him in Good Old Boat magazine.