
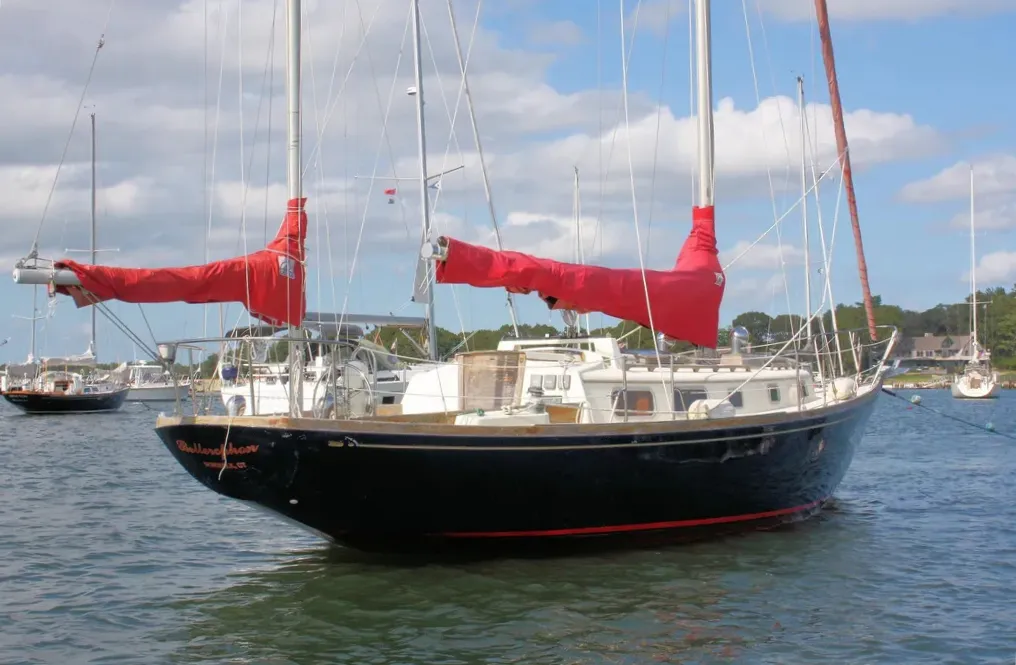
The Bristol 39 and Bristol 40 are basically the same boat, even though the specifications state that the Bristol 40 is nearly a foot longer than the Bristol 39. According to the builder, the hull sections aft were made slightly fuller on the Bristol 40, and the stemhead fitting was altered. After very careful scaling of plans, we can say with reasonable confidence that from one end of the hull to the other, excluding the bow pulpit and the anchor roller, the Bristol 39 and Bristol 40 are about 39-ft. 8-in. long. Whether you call it a 39-footer or a 40-footer is up to you.
But this is not a 40-ft. boat in the modern sense. Yes, if you take a tape measure to the boat, you’ll read almost 40 ft. But if you go below, you’ll swear you stepped onto a 33-ft. boat—at least if you’re used to looking at the 33-footers built today.
History
With a waterline length of 27 ft. 6 in. and a beam of 10 ft. 9 in., the Bristol 40’s proportions are about as typical as you can get of cruising/racing sailboats built between about 1930, when the CCA (Cruising Club of America) rule was conceived, and 1970, when it was replaced by the International Offshore Rule (IOR). For those 40 years, about 30 percent of the average boat’s length was in overhangs. Today, you find the waterline length and beam of the Bristol 40 on boats less than 35-ft. long.
About 150 Bristol 40s were built. This does not include the relatively small number of boats in the Bristol 39 series.
The 39 was one of the first models built by Bristol Yachts, entering production in 1966. Beginning with 1972 models, the boat was rechristened the Bristol 40. The last Bristol 40 was built in 1986.
If you like traditional yachts, you’ll find the Bristol 40 appealing. The boat has the long overhangs, lovely sheerline, low freeboard, narrow cabin trunk undistorted hull shape, and narrow beam we associate with the beautiful yachts of the past. If you didn’t know she was a Ted Hood design, you might mistake her for a boat by Olin Stephens, John Alden or Phil Rhodes. The trade-off for these traditional good looks is a boat with a small interior compared to today’s 40-footers.
Sailing Performance
“Fast” is a very relative term when you’re talking about sailboats. The Bristol 40 is not fast relative to more modern 40-footers, but her performance is similar to that of other boats of her length built under the CCA rule, when boats were heavier and shorter on the waterline than they are today. The boat is close in speed, for example, to the Hinckley Bermuda 40 yawls with the original low aspect ratio rig. It is about 30 seconds per mile slower, however, than the Cal 40—a boat of the same length on deck, but with a longer waterline, less wetted surface and slightly less displacement.
Stability
In both keel and centerboard versions, the Bristol 40 is a fairly tippy boat, as you would expect from her narrow beam, shoal draft, and modest amount of ballast. Like “fast,” however, “tippy” is a relative term.
Most narrow boats have relatively low initial stability, even if their ultimate stability is good. For example, the McCurdy and Rhodes 62-footer Arcadia, built in 1972, is about 2 ft. narrower than a new IOR 60-footer would be, and has a righting moment about 15 percent lower than that of the new boat, even though Arcadia is significantly heavier.

Yet Arcadia’s range of positive stability is about 143 degrees, while the typical “modern” racer/cruiser loses positive stability at 120 degrees or less.
Unfortunately, being narrow and tippy doesn’t guarantee a good range of ultimate stability. The keel version of the Bristol 40 loses positive righting moment at about 120 degrees—the absolute minimum we would consider for a serious offshore cruiser. The centerboard version’s range of stability is less—about 110 degrees for the only boat rated under the International Measurement System (IMS).
It is not unusual for centerboarders to have very low positive stability. The Hinckley Bermuda 40—the classic keel-centerboarder—typically loses stability at an even lower angle than the centerboard Bristol 40, yet few people would consider the boat unsuitable for passage making.
Sail Plan
Owners report that the Bristol 40 is very sensitive to the amount of sail carried. We’d suggest a modern headsail reefing/furling system for shorthanded cruising to reduce the number of headsail changes required. Like most CCA boats, the Bristol 40 is a good reaching boat, lacking the rounding-up tendency of many modern boats with full sterns. The trade-off is that the boat tends to squat when running downwind, digging a hole that’s hard to climb out of. A Bristol 40 with a full keel won the 1983 Marion-Bermuda Race, an event that consisted largely of four days of close reaching in light to moderate breezes.
Genoa Track
Because the boat is narrow, there is no need to move the genoa track inboard of the toerail. The only real disadvantage of toerail-mounted genoa track is that you may have to relead the sheet to clear stanchions when changing headsails or reducing sail area with a headsail furler, unless there are turning blocks at the aft end of the genoa track. The two most common mainsheet arrangements on the boat are a short traveler spanning the cockpit immediately in front of the steering wheel, or a longer traveler over the coachroof in front of the companionway. The short traveler in the cockpit doesn’t really offer much mainsail control, but it is a convenient location for the sheet.

Rig
The rig is a basic masthead sloop or yawl, using an untapered, keel-stepped anodized mast with single spreaders and double lower shrouds: basically foolproof. The lower shroud chainplates do not line up exactly with the pull of the shrouds, which will tend to fatigue the chainplates over time, as well as increasing the likelihood of leaks due to an unfair pulling angle.
Since this is a boat that was in production for the better part of 20 years, it’s difficult to generalize about the sailing gear you’ll find. On the Bristol 40s we’ve looked at, the stock winches tend to be one or two sizes smaller than we’d put on the boat today. You’re unlikely to find self-tailers on older models.
Yawl Option
A lot of Bristol 40s were built as yawls. While the yawl rig is pretty and looks very traditional, the mizzen is generally only useful to help balance the helm, as a convenient place to mount a radar antenna, and to serve as a support for a mizzen staysail on the rare occasion that it pays to carry one. The mizzen makes the boat more tippy and increases windage—disadvantages for upwind sailing.
Engine
Before 1970, Bristol 39s came with either Atomic 4 or Graymarine gas engines. Later model 39s and Bristol 40s were powered either by the Atomic 4 or by a variety of diesels, including the Westerbeke 4-91, Westerbeke 4-107 and 4-108, Perkins 4-108, or Volvo MD2B and MD3B engines. That should be enough variety to satisfy everyone.
The Westerbeke and Perkins 4-108s are essentially the same engine, and in our opinion would be the best engine for the boat, although they’re more power than it needs. Diesel engine installations in the Bristol 40 are not without problems. There is little room between the shaft coupling and the stuffing box—so little, in fact, that several owners surveyed reported that it is almost impossible to reach the stuffing box for adjustment or repacking.
Fuel Tank
In all models, the fuel tank is located under the cockpit sole, above the engine. Fuel capacity is about 30 gallons. Early diesel-powered models have black iron fuel tanks, and at least one owner surveyed reported having to replace a rusted-out tank after a years. Later models have aluminum fuel tanks, which are less likely to corrode. Range under power with the Perkins 4-108 and 30 gallons of fuel will be about 180 miles.
Prop Size
The gasoline engines used in early models swing a small prop. Unfortunately, when the switch was made to bigger diesels—the Perkins 4-108 displaces 108 cubic inches, the Atomic 4 only 65 cubic inches—the propeller aperture was not enlarged, limiting prop size. We measured the height to be 16 1/2 in., which means you can really only swing about a 15-in. prop and still maintain adequate tip clearance. The result is that you end up turning an oversquare prop (more pitch than diameter), which is not the most efficient way to utilize the engine in a sailboat.
Our prop choice would be a three-bladed feathering Maxprop for the best combination of performance under both sail and power. The Maxprop would also slightly improve handling in reverse, which is rated as poor by most owners. A tiny fixed prop tucked in an aperture in the deadwood and rudder is a bad combination for handling in reverse. Powering ahead, the boat handles just fine.
Insulation and Access
There is no sound insulation in the engine compartment. Access to the front of the engine is fair, requiring removal of the front of the engine box which doubles as the companionway ladder.
Construction

Bristol Yachts has gone through a lot of changes over the years. The prime mover behind Bristol was Clint Pearson, one of the pioneering Pearson brothers—the other, Everett, now runs Tillotson-Pearson.
The boats built by Bristol today are a far cry from those of 15 years ago. Current Bristols are targeted toward the middle to upper end of the production and semi-custom markets, with very good finish detail and systems. Originally, Bristols were aimed at the mass market, and were finished and equipped accordingly.
Since the Bristol 40 was built over a period of 20 years, there were a number of minor changes during the production run, but the last boats are essentially the same as the first ones.
Weight
The Bristol 40 is not a particularly lightly built boat, but she is certainly not heavy for her overall length, even by modern standards. The boat is substantially lighter than most long-keel CCA 40-footers. The Hinckley Bermuda 40, for example, displaces about 20,000 lb. in normal trim. The Cal 40, considered a real lightweight in 1966, weighs about 16,000 lb. in IMS measurement trim; the average Bristol 40, right at 17,000 lb. in the same configuration.
By way of comparison, the Little Harbor 38 that won the 1986 Newport-Bermuda Race tips the scales at a hefty 25,000 lb., and the newer Bristol 38.8 has a designed displacement of just over 19,000 lb.
Quality Control Issues
None of the Bristol 40 owners we surveyed report any major structural flaws. They do, however, complain of annoyances such as leaking ports, deck hardware, and hull/deck joints. These are generally assembly and quality control problems, and most can be solved by the owner, albeit with a fair amount of labor. A leaking hull/deck joint may be more of a problem, but this type of leak should show up during a careful examination of the boat. Discoloration and water streaks inside lockers and on bulkheads, rust and drips on through-fastenings, and mysterious puddles of water may indicate leaks in the joint.
Water Capacity
From a cruiser’s point of view, a nice feature of the Bristol 40 is its water capacity: 130 gallons in two fiberglass water tanks.
Plan for Gelcoat Upgrades
Any sailboat hull older that about eight years is getting on toward being a candidate for painting. While the gelcoat in the Bristol 40s we examined still looks reasonable, most of the colored hulls—pastels were popular in the 70s—are badly faded. The colored gelcoat used was not colorfast.
We also noted numerous gelcoat flaws on decks cracks around stanchion bases, some voids at sharp corner transitions. During the survey, the surveyor should carefully sound the entire deck for voids. If you’re going to go to the trouble and expense of painting, you might as well catch all the problems at the same time.
Deck
Deck non-skid is a molded-in basket weave pattern, and we have found it to be less effective than more aggressive non-skid designs.
Cockpit
The cockpit is huge, with seats almost 7-ft. long. The well is narrow enough that you can brace your feet against the opposite seat—a good feature on any boat, but especially important on a tippy boat. The big cockpit is a mixed blessing. It gives plenty of space for daysailing or in-port parties, but it is also vulnerable to filling in extremely heavy offshore conditions.
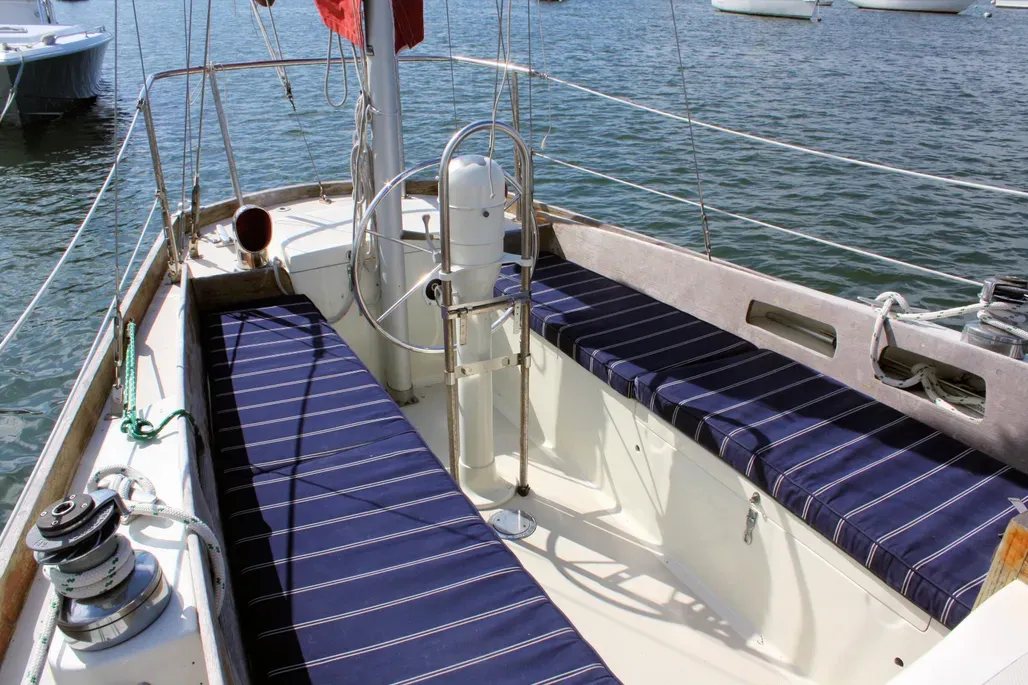

In our opinion, the cockpit scuppers are too small. Each of the two scuppers is about the size of a bathtub drain. Since there is no bridgedeck—just a raised companionway sill—it is particularly important that the cockpit drain quickly. This is a pretty reasonable retrofit job. For offshore sailing, the bottom dropboard should be caulked and permanently secured in place.
Teak
There is a reasonable amount of exterior teak trim on the boat, including toerails, cabin eyebrow trim, handrails and cockpit coamings. A Bristol 40 with a freshly-Awlgripped hull and varnished teak trim would look handsome, indeed.
Fittings
On the port and starboard quarters, there are large chocks for dock lines. While these look substantial, they are only screwed to the toerails, and can easily tear out. Chocks can be very heavily loaded during panic dockings, and should always be through-bolted, as should all deck hardware.
Through hull fittings are not recessed flush, but can easily be faired in to reduce drag in very light air. The Constellation-style rudder is set slightly above the aft edge of the keel, so that the boat will ground out on the keel rather than the rudder.
Keel
Instead of a bolt-on external keel, the Bristol 40 has a molded keel cavity filled with 6,500 pounds of lead. One owner we surveyed had added 1,500 lb. of lead pigs in the bilge to improve stability.
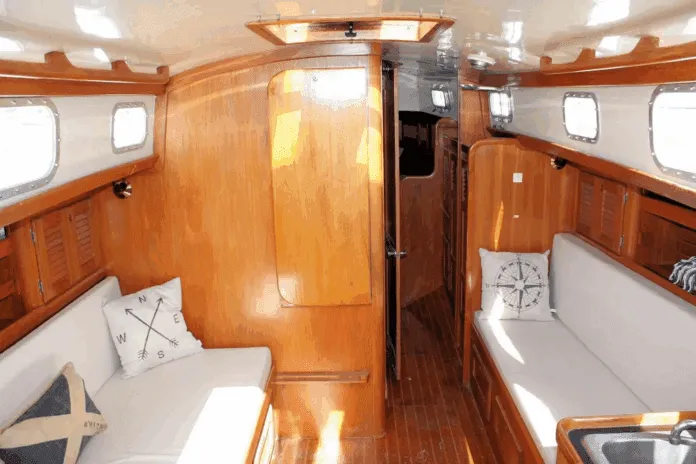
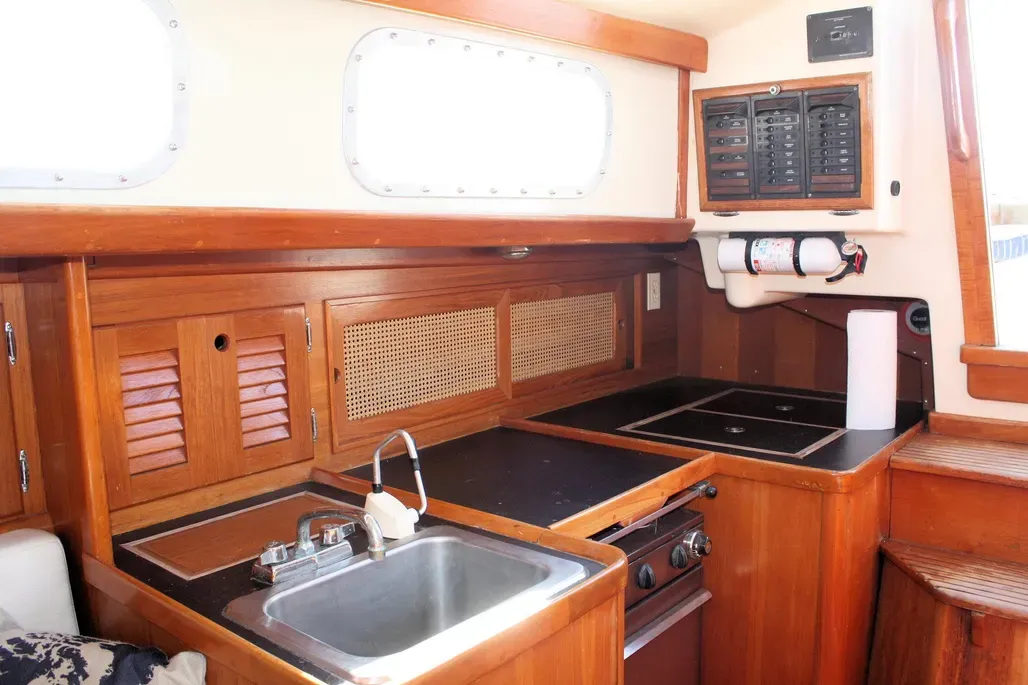
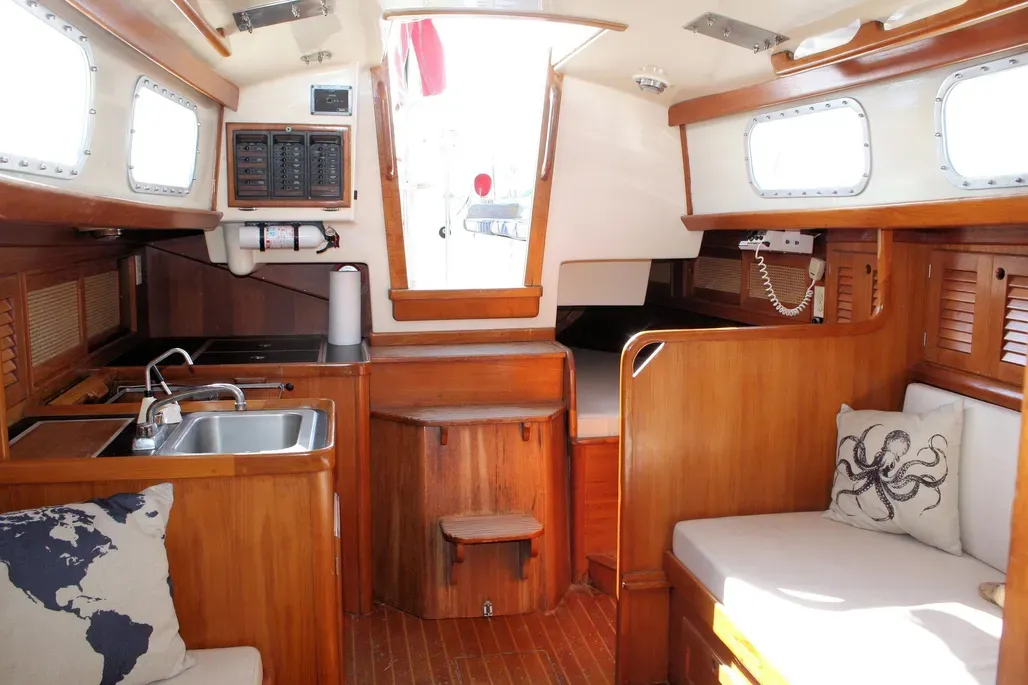
Bristol has always made extensive use of built-up interiors of plywood and solid wood, rather than fiberglass molded components trimmed out in solid wood. The company has also made extensive use of mahogany rather than teak in interior construction. If you’re used to the dull brown of teak, the brighter reddish-brown of the mahogany interior of the Bristol may or may not appeal to you. Mahogany must be varnished: it is not suited to an oil finish in a marine environment. If you let the varnish wear off, the wood will turn grey, particularly after exposure to water. At the same time, mahogany is lighter and brighter than teak, and can make an all-wood interior slightly less gloomy. If all else fails, you can always paint out the mahogany bulkheads and leave the mahogany trim varnished. Teak plywood is much harder to paint out, since its waxy surface doesn’t hold paint very well. The built-up interior allowed a number of interior options in the Bristol 39 and 40. As originally drawn, the boat had a wide-open offshore racing interior, with a sail locker forward, the head in the area normally reserved for a forward sleeping cabin, and symmetrical pilot berths, settees, and quarterberths in the main cabin. While it provides six sea berths, this interior has little appeal for a cruising family. Most boats were built with one of several more conventional interior layouts. Opposite the head are the usual hanging lockers. Several different main cabin layouts were offered, with an arrangement to please just about every fairly conventional taste. On the port side, you’ll find either a settee berth with storage outboard, a U-shaped dinette, or a narrow pull-out settee with a pilot berth outboard. On the starboard side, you’ll usually find a settee with a folding pipe berth above, although some boats were built with a conventional pilot berth outboard of the starboard settee. On boats without a dinette, the main cabin table folds up against the port forward bulkhead—a reasonable solution in a narrow boat. Main cabin storage space is quite good, with a number of drawers and lockers. The actual storage arrangement varies with each interior layout. Ventilation in the main cabin, as well as in the entire boat, is so-so. There is an opening port in the head, and a cowl vent overhead. There is another cowl vent on the other side of the cabin trunk opposite the head, providing some air to the forward cabin and main cabin in foul weather. Over the forward cabin is a large fiberglass hatch. A fiberglass hatch over the main cabin was optional. The main cabin ports do not open. Ventilation would be greatly improved by adding Dorade boxes just in front of the dodger breakwater at the aft end of the main cabin. If you also put a reversible aluminum-framed hatch directly over the middle of the main cabin, and added a small dodger to it for heavy weather protection, you’d go from lousy ventilation to good airflow in one fell swoop. We’re not keen on the fiberglass hatches used in production boats in the 1970s. They distort easily, and never seem to seal completely. Headroom is about 6 ft. 4 in. on centerline aft, decreasing to about 6 ft. in the forward cabin. In all interior layouts other than the original ocean racing one, the galley is at the aft end of the main cabin. There are two aft galley arrangements. One is spacious but not particularly efficient, the other is tight. On boats equipped with a quarterberth and nav station on the port side, the galley is jammed into the starboard aft corner, and is small for a 40-footer. On boats without a nav station, stove and sink are on the port side, with a large icebox opposite to starboard. The top of the icebox is then used as a navigation table. Neither galley layout is as good as the Ushaped galley used on more modern boats such as the Bristol 38.8. You’ll have to make a choice on the galley layout. A nav station is very desirable if the boat is used for more than daysailing. Yet the starboard galley you get on boats with nav stations is quite small, and doesn’t have much storage for foodstuffs or utensils. Even on boats with the port nav station, the electrical panel is located on the starboard side, above the galley and next to the companionway, in a fiberglass box that’s a molded part of the cabin liner. We’d want to give better protection to the panel by building a frame with an opening clear acrylic cover. Despite the narrowness of the Bristol 40 compared to newer boats, the interior is reasonably laid out and not cramped. Headroom is good, and you can easily make improvements in ventilation. The interior doesn’t seem as spacious as a lot of boats due to the fairly narrow, tall cabin trunk. Newer designs have more freeboard, allowing a lower cabin trunk and increasing the feel of interior space. Like the better-known Bermuda 40, the Bristol 40 is an exceptionally pretty boat, and those good looks are one factor that kept the boat in production for such a long time. But the Bermuda 40 has been carefully refined, and its reputation nurtured by a group of nearly-fanatical owners who are willing to pay rather remarkably high prices for a design that is now 30 years old. The Bristol 40, on the other hand, lacks that reputation and following. A few Bristol 40s were built for die-hards even after the boat was superseded in 1983 by the faster, roomier, stiffer Bristol 38.8—a design that is a distinctly more modern Hood cruiser/racer. Because of her large cockpit, small cockpit drains, slightly vulnerable companionway, and fairly low initial stability, this boat wouldn’t be a good choice for extended offshore cruising, although Bristol 40s have certainly done their share of it. For cruising in the Chesapeake, Bahamas, or Gulf of Mexico, the keel-centerboard version would be a reasonable choice, and even the deep keel model draws substantially less than most 40-footers. A late-model, sloop-rigged boat with Perkins or Westerbeke diesel would be our first choice. Since relatively few changes were made in the boat during the years of production, however, you might also find a good older boat on which a lot of attention has been lavished. If you like traditional looks, and you cruise in shoal coastal waters without extremely heavy winds a lot of the time, the Bristol 40 should appeal to you. You’re a natural candidate for the boat if the looks of the Bermuda 40 catch your eye, but you don’t have the pocketbook to indulge yourself in Hinckley quality.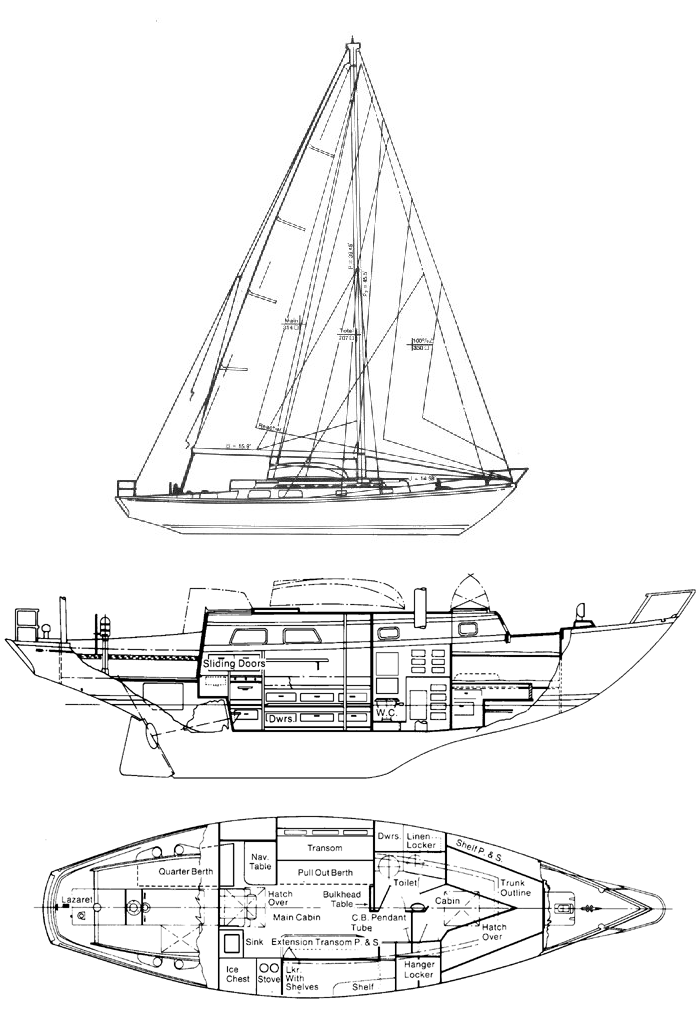
Courtesy of Sailboatdata.com Bristol 40 Bristol 39
Hull Type: Modified Full Keel Long Keel
Rigging Type: Masthead Sloop Masthead Sloop
LOA: 40.16 ft / 12.24 m 39.00 ft / 11.89 m
LWL: 27.54 ft / 8.39 m 27.54 ft / 8.39 m
S.A. (reported): 694.00 ft² / 64.47 m² 648.00 ft² / 60.20 m²
Beam: 10.75 ft / 3.28 m 10.75 ft / 3.28 m
Displacement: 17,580.00 lb / 7,974 kg 17,580.00 lb / 7,974 kg
Ballast: 6,500.00 lb / 2,948 kg 6,500.00 lb / 2,948 kg
Max Draft: 5.37 ft / 1.64 m 5.40 ft / 1.65 m
Construction: FG FG
Ballast Type: Lead Lead
First Built: 1970 1966
Last Built: 1986 1970
# Built: 149 58
Builder: Bristol Yachts Inc. (USA) Bristol Yachts Inc. (USA)
Designer: Ted Hood Ted Hood/Dieter Empacher
Make: Universal Perkins
Model: Atomic 4 4107
Type: Gas Diesel
HP: 30 37
Fuel: 31 gals / 117 L 25 gals / 95 L
Water: 130 gals / 492 L 130 gals / 492 L
S.A. / Displ.: 16.49 15.39
Bal. / Displ.: 36.97 36.97
Disp: / Len: 375.73 375.73
Comfort Ratio: 36.68 37.09
Capsize Screening Formula: 1.66 1.66
S#: 1.16 1.16
Hull Speed: 7.03 kn 7.03 kn
Pounds/Inch Immersion: 1,057.84 pounds/inch 1,057.84 pounds/inch
I: 45.50 ft / 13.87 m 45.50 ft / 13.87 m
J: 14.58 ft / 4.44 m 14.60 ft / 4.45 m
P: 39.45 ft / 12.02 m 39.50 ft / 12.04 m
E: 16.00 ft / 4.88 m 16.00 ft / 4.88 m
S.A. Fore: 331.70 ft² / 30.82 m² 332.15 ft² / 30.86 m²
S.A. Main: 315.60 ft² / 29.32 m² 316.00 ft² / 29.36 m²
S.A. Total (100% Fore + Main Triangles): 647.30 ft² / 60.14 m² 648.15 ft² / 60.22 m²
S.A./Displ. (calc.): 15.38 15.40
Est. Forestay Length: 47.78 ft / 14.56 m 47.79 ft / 14.57 m
Interior
Layout Options
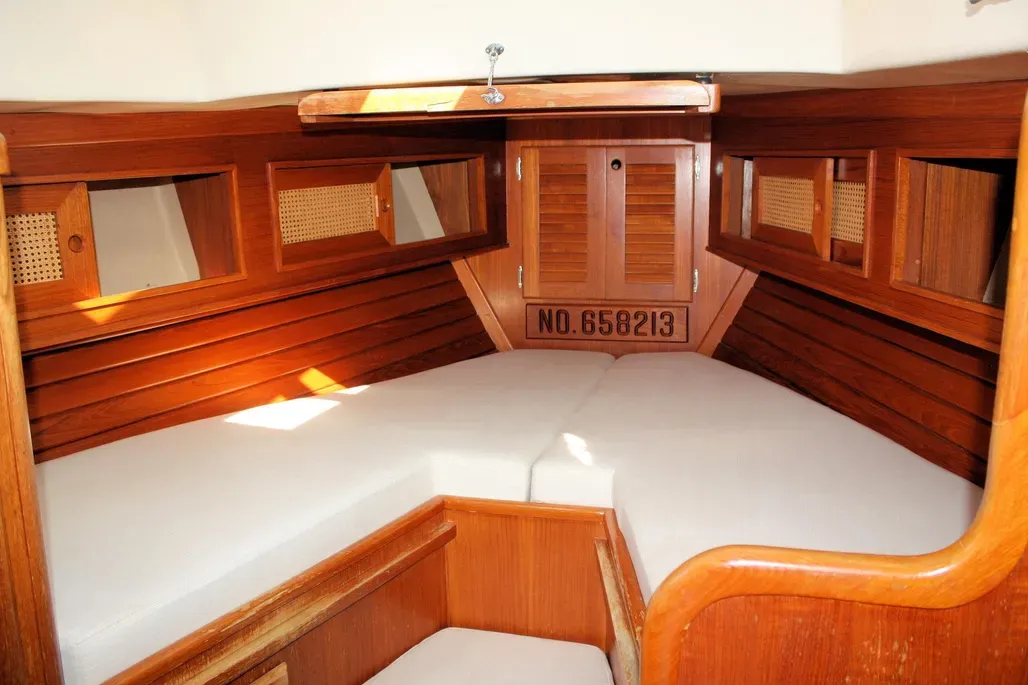

Ventilation
Galley

Bottom Line
Conclusions

Market Scan Contact
1982 Bristol 40 Lawson Yachts LLC
$25,000 USD 781-423-3247
Marion, Massachusetts Yacht World
1972 Bristol 40 Vital Force Yachting
$15,000 USD 842-250-6950
New Hamburg, New York Yacht World
1972 Bristol 40 Sailboats Northeast
$39,500 USD 781-631-4910
Salem, Massachusetts Yacht World











The big problem when looking at the cost of boats is that manufacturing costs are primarily determined by weight. It costs $X PER TON to build a boat, almost regardless of its dimensions. This means that a super light, cheaply built 40-footer can cost less than a well-built 30-footer. Many potential buyers look at the accommodation space, not the performance, and so think the lightweight boat looks much better value. Whether it is depends on what you want to do with it.