The Nonsuch 30 is an oddity. She is a fin keeled, spade ruddered boat with an unstayed wishbone cat rig. Weird.
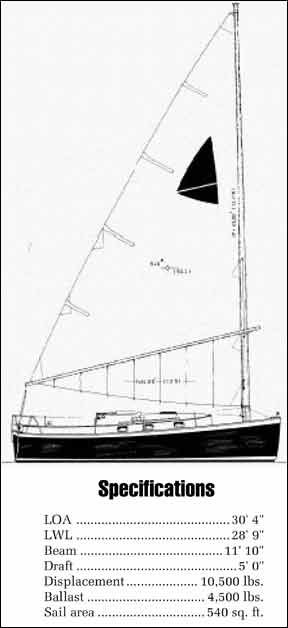
She was built in Canada, whose main boatbuilding export has been C&C sailboats. Come to think of it, all her construction details look very much like those of C&C boats. This isn’t unusual, since George Hinterhoeller, the builder, was formerly the president of C&C, and one of the founders of the three company merger that created C&C Yachts.
When Hinterhoeller left C&C to recreate Hinterhoeller Yachts Ltd., he took with him those characteristics that have given C&C a reputation for quality: good attention to finish detail and high-quality balsa-cored hull construction.
The Nonsuch 30 is the concept of retired ocean racer Gordon Fisher, the design of Mark Ellis, and the created child of Hinterhoeller, who is one of the few production boatbuilders with the legitimate title Master Boatbuilder, earned the hard way through apprenticeship in Europe.
The Nonsuch 30 was originally a Great Lakes phenomenon, which is to be expected considering her origins. She proved quite popular elsewhere, however. This is not surprising considering the amount of boat that has somehow been slipped into an LOA of less than 31′.
Production of the Nonsuch line ceased in 1989.
Construction
George Hinterhoeller’s reputation as a builder is not unearned. His balsa-cored hulls are known for being light and strong. It is probably not an exaggeration to say that he knows as much about cored construction as any boatbuilder around.
Both hull and deck of the Nonsuch 30 are balsa cored. The hull and deck are joined by a through-bolted butyl-bedded joint capped with an aluminum toerail. The butyl tape used for this purpose has no real structural properties, but does create a good watertight seal. A sealant such as 3M 5200 provides equivalent sealant properties with greater structural properties, and we prefer its use in hull-to-deck joints. It is hard to quibble with the Nonsuch’s strongly through-bolted joint, however.
The external lead keel is bolted on with stainless steel bolts. These pass through floor timbers of unidirectional roving, transferring keel loading from the garboard section to a greater area of the hull.
The cockpit seats and coamings contain a surprisingly large number of sharply-radiused turns. Gelcoat cracks are likely to develop here earlier than anywhere else in the hull.
The freestanding mast requires modification of normal construction methods. While no chainplates are required, substantial bulkheading is required in the area of the mast to absorb the considerable forces generated by the unstayed mast. The forward six feet of the hull is strongly bulkheaded for this purpose, and no sign of undue strain could be detected.
Because there is no rigging to hold the mast in the boat should she capsize, alternative means must be found. This is accomplished by lagging a cast aluminum, hexagonally-shaped female mast step to the hull. The butt of the mast is fitted with a hexagonal male counterpart which is strongly joined to the mast step by stainless steel hex-head set screws. The mast is further connected to the hull by a deck-level pin which passes through the mast and the cast aluminum deck collar. Deck hardware is properly backed for load distribution.
There are a few surprising shortcomings. The aluminum rudder quadrant stops have sharp edges which could easily cut into the exhaust line inside the cockpit lockers. This could happen—it had happened on the boat we sailed—if the upper rudder retaining nut is loose, allowing the rudder to drop down slightly. Gate valves are used on most through hull fittings below the waterline, rather than seacocks or ball valves, and no valves at all are fitted on drains and exhaust lines at the bottom of the transom, despite the fact that they could be submerged in a heavily loaded boat.
Despite these deficiencies, construction is generally to very high standards, well above average for the industry.
Handling Under Sail
The Nonsuch 30 is one of the most boring boats we have ever sailed. Tacking requires no yelling, releasing of sheets, cranking, tailing, or trimming. The helmsman simply says “I think we’ll tack” and gives the wheel a quarter turn, being careful not to upset his Mt. Gay and tonic. Nonsuch quietly slides through about 85 degrees and settles on the other tack with a minimum of fuss. Beating up a narrow channel simply requires repeating the above process.

The person who learns to sail on a Nonsuch 30 will receive a rude awakening when switching to a more athletic boat—which means almost any other 30 foot sailboat. The Nonsuch 30 is simply one of the easiest boats to sail we’ve seen.
This doesn’t mean that it’s necessarily easy to sail well. Getting the most out of the boat upwind definitely requires some practice. The aluminum mast is quite flexible, allowing the top of the mast to fall off as the wind increases. The sail’s draft will shift, changing its efficiency. In about 10 knots of breeze, the top of the mast falls to leeward about a foot. This can be a little disconcerting to those used to a fairly rigid stayed mast.
Sail shape is controlled by the “choker,” a line which controls the fore and aft trim of the wishbone and functions as a clew outhaul. Tensioning the choker pulls the wishbone aft, flattening the sail. The sail is slab reefed pretty much the same as a conventional mainsail.
The Nonsuch mainsail is 540 square feet, with a hoist of 45 feet and a foot of 24 feet. By way of comparison the mainsail of the Irwin 52 is 525 square feet, and that of the Cal 31 210 square feet. The sail does not handle like a sail of 540 square feet, fortunately. The wishbone is rigged with permanent lazy jacks which hold the sail as it is dropped.
Furling merely involves putting ties around the neatly cradled sail for the sake of aesthetics. Dousing the main or reefing is easily accomplished by one person, as all of the sail controls lead back to the cockpit.
The Nonsuch does not suffer from “catboat disease”—the tendency to develop monstrous weather helm as the breeze pipes up. She is, rather, remarkably well mannered, with a surprisingly light helm in the light to moderate winds in which we sailed her. Downwind she held course with the wheel brake off and hands off the wheel. Her performance was almost as good upwind at moderate angles of heel.
She is a stiff boat. The flexible mast allows a substantial amount of air to be spilled from the main as the wind pipes up, removing much heeling force. We found that the boat went better upwind with a reef in the main even at moderate angles of heel once the upper mast began to fall off. Getting sail off the more flexible upper part of the mast allows better draft control as the wind increases.
Having only one sail can be a real nail-chewer to the uncured racer. Whether it blows five knots or 25, the maximum amount of sail you can have is already up. Some unreconstructed racers have equipped the Nonsuch 30 with a blooper for light air downwind performance.
The Nonsuch 30 is no Cape Cod catboat under the water. She has a moderate aspect ratio fin keel, low wetted surface, and a freestanding semi-balanced spade rudder. These characteristics greatly add to her performance.
With all sail controls led back to the cockpit, she is a natural candidate for singlehanding. We strongly recommend the optional self-tailing winches for all functions if shorthanded sailing is contemplated.
The Nonsuch 30 is not the boat for the hard-core grand prix racer. Her entire sail inventory consists of that one big sail, with perhaps, but not necessarily, a single downwind sail. You will not become the bosom buddy of any racing sailmaker by owning a Nonsuch. Then again, no sailmaker will ever have a second mortgage on your boat, either.
Handling Under Power
The Nonsuch 30 was originally equipped with a 23 horsepower Volvo MD 11C diesel with saildrive. This basically eliminated engine installation and alignment problems for the builder, saving both time and money.
These units have an integral cast zinc to protect the vulnerable aluminum lower unit from galvanic corrosion. A special Volvo-supplied zinc is required—not an item that you can pick up in any boatyard. About hull number 125, this installation was changed to a more conventional engine and shaft arrangement, utilizing a new 27 horsepower Westerbeke diesel.
Either engine will drive the boat to hull speed. We greatly prefer the conventional engine installation, which is understood and can be worked on by most boatyards. It is less vulnerable to corrosion, and runs quietly and smoothly.
Because of her high freeboard the Nonsuch 30 will be susceptible to crosswinds when docking. With most of her windage forward she will have a tendency to blow bow downwind. A good hand on the throttle and gearshift will be a real plus in tight docking situations. Without the complication of wind we found her easy to back down into a slip once a sharp burst of throttle was given to activate the folding prop with which our test boat was equipped.
Deck Layout
Because the Nonsuch 30 has no standing rigging, her side decks are devoid of obstacles. Because she has no headsails there are no sheeting angles to be concerned with.
For cruising the optional bowsprit/anchor roller with hawsepipe to the otherwise unusable forepeak is highly desirable. Otherwise, anchor and rode must be stored in one of the cockpit lockers and dragged forward every time you wish to anchor. We also recommend the installation of a bow pulpit. With no shrouds to hold when forward there is a great feeling of vulnerability on the bow. These things may make the Nonsuch 30 un-catboatlike in appearance, but they will greatly add to the safety and convenience of both sailing and anchoring.
The cockpit of the Nonsuch 30 is large and deep. It is not particularly comfortable, and without four inch or thicker cockpit cushions it is impossible for a person of average height to see forward over the cabin. The helmsman’s position is elevated above that of the other seats, but visibility even from that position is only fair.
With the standard white-on-white gelcoat scheme the cockpit of the Nonsuch 30 is sterile and generates a lot of glare on sunny days. The optional contrasting nonskid and teak cockpit grate alleviates part of this problem.
The large cockpit creates other problems. First, you should never raft up with other boats at anchor. A friendly crowd of eight could easily fit in the cockpit.
There are more serious problems associated with the cockpit design. The Nonsuch 30 is promoted as a “new offshore concept.” We think this is an unfortunate choice of words, because the standard cockpit is not suited to offshore use. There is no bridgedeck. The companionway goes almost to the level of the cockpit sole—about three feet below the level of the lowest point in the cockpit coamings. Coupled with the huge cockpit volume, this creates a situation that cannot in any good conscience be called an offshore configuration. If this boat is to be called an offshore sailboat, we think there should be an optional cockpit arrangement—a large bridgedeck which could incorporate life raft storage, two more large cockpit drains, and perhaps a raised cockpit sole to further reduce the cockpit’s volume.
There are three cockpit lockers; deep port and starboard lockers, and a lazarette propane locker set up to hold two ten-pound gas bottles. The large side locker should incorporate some form of easily-removed retainer system to prevent items there from rolling under the cockpit.
On the boat we sailed the drain line from the propane locker overboard was too long. At the low point in the loop water had collected in the hose, which exits through the transom and is underwater in many sailing conditions. This water prevents any propane leakage from draining overboard as designed. The hose should be shortened to remedy a potentially hazardous situation.
When tacking or jibing it is easy for the helmsman to get caught by the mainsheet as the boom comes over. A better lead would be welcome here, perhaps having the mainsheet system incorporated into the stern rail.
Interior
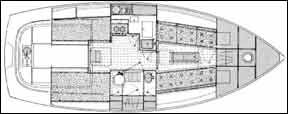
The interior volume of the Nonsuch 30 is an eye opener, even to those used to the modern trend toward maximum interior volume on minimum overall length. To anyone used only to the interior space of an older boat, the interior of the Nonsuch 30 is absolutely stunning.
The waterline and beam of the Nonsuch 30 are about the same as that of a modern 36 foot cruiser-racer, and that beam is carried quite a bit further forward. Coupled with high topsides and a highly-crowned deck house, this yields a boat with tremendous interior volume for her overall length.
The interior layout is unusual but practical. There is no forward cabin in the conventional sense. This isn’t a real drawback. The forward cabin on the typical 30 footer is only useful for sleeping or sail stowage, and frequently has berths which narrow so much forward that an all-night game of footsie for the occupants is a necessity rather than a pleasure.
The forwardmost six feet of the boat is given over to two huge hanging lockers and a great deal of storage space which has been created by the three transverse and two fore and aft bulkheads that stiffen the hull in the way of the mast. This storage space is not readily accessible, and will probably end up as the boat’s attic, collecting little-used piles of gear until the day when it must be all removed to get at the mast step to remove the mast.
The rest of the boat is basically one large cabin. What would be considered the main cabin occupies the forward third of the interior. At the forward end are the aforementioned hanging lockers and a bureau. There are shelves and bins outboard of the two long settees that face each other at a comfortable distance across the cabin, with a dropleaf table on centerline. Varnished pine ceiling behind the settees is a welcome note in an otherwise dark teak interior.
The galley is to port midships. The cook is out of the traffic flow yet located in the center of activity if there are people both below and topsides. The galley has a gimballed propane stove with oven, a well-insulated icebox with (hurrah!) an insulated, gasketed lid, and a deep sink nearly on centerline which will easily drain on either tack. The icebox melt water is pumped into the galley sink. For the sake of aesthetics the icebox drain should tee into the sink drain below the sink, relieving the cook of the dubious pleasure of watching the things which dribble to the bottom of the icebox flow through the sink.
The head is opposite the galley. Because of the pronounced deckhouse camber, headroom there decreases rapidly as you move outboard.
An unusual option was a demand propane-fired hot water heater. This compact unit mounts on a head bulkhead, and has electric ignition. When a hot water faucet is turned on the heater fires, and will heat steaming hot water as fast as the water pressure system will deliver it. This is much less complicated than the normal engine water heat exchanger/110 volt powered water heaters found on most boats. Since the boat is already plumbed for propane, installation of this heater is straightforward.
There are quarterberths port and starboard aft of the galley and head. The standard berth starboard is a double, with a single to port. An option provides doubles on both sides, although filling all the berths on the boat requires an open mind and no highlydeveloped sense of privacy.
Despite the open interior of the boat, privacy can be attained through another unusual interior option. A hidden slide-up partition can be installed between the galley and the forward/main cabin, and a bifold louvered teak door which folds up against the head bulkhead. When closed, the door and partition divide the boat into two large compartments for sleeping, with reasonable separation between them.
The occupants of the thus-created forward cabin must enter the aft cabin either to go on deck or to use the head, an inconvenience.
Like the cockpit, the huge interior invites company. In the event of a sudden rainstorm, the eight people who previously occupied your cockpit could easily move below to continue their revelry. If there were already eight below—a not unlikely circumstance—you may be in trouble. Sixteen people is too many belowdecks even in the Nonsuch 30.
Ventilation of the interior is excellent, with seven opening ports, two hatches, and two dorade boxes. The propane heater vents overboard through its own exhaust stack.
Conclusions
The Nonsuch 30 is an unusual boat by any standards. The unstayed wishbone cat rig is becoming increasingly popular. It does greatly reduce the cost of sails, spars, and rigging.
The general appearance of the boat is similar to a traditional catboat, although she will never be taken to be a product of the Crosby yard. Her generally catboatlike hull dimensions produce the maximum hull volume on a minimum overall length.
Despite her billing we do not consider her an offshore cruiser with her standard cockpit arrangement. She will make an excellent coastal cruiser for a couple or family with up to three small children or two older children.
Because she is easy to sail and rig, has a big cockpit and a roomy, well-ventilated interior, she should make a good Caribbean charter boat for two couples, although head access is a minor problem from the forward cabin. Surprisingly, none have entered the southern charter business.
The Nonsuch 30 is not a traditionalist’s catboat. She lacks the sweeping sheer, low freeboard, gaff rig, and barndoor rudder of the Cape Cod catboat. She also lacks that boat’s infamous sailing characteristics—ferocious weather helm, inability to go to windward, and a man-killing mainsail.
She is a relatively simple, easily sailed boat for the convivial sailor who doesn’t mind being seen in what many might consider an oddball boat with an oddball interior and an oddball rig, The more you look at it, the less oddball it seems.




































Hi, Hope you are safe and well. We Provide Estimation – Quantities and materials takeoff for all kinds of constructions, Excavation, Foundation, Interior and exterior renovation, roofing projects etc. You can email us the plans in PDF or via Google Drive, Drop box link or any other link where from we can download them. Thanks