
Bill Lapworth didn’t invent light-displacement cruiser-racers, but his name is indelibly linked with the type. At 15,000 pounds of displacement on a 30′ waterline, the Cal 40 is still a fairly light boat, especially considering the low-tech materials and techniques available when she was introduced. Lapworth designed a number of smaller sisters to the Cal 40 in the late 1960’s, all looking as alike as peas in a pod.
If imitation is the sincerest form of flattery, then Lapworth should have been very flattered at the interest his Cal designs generated, for Frank Butler, now owner of Catalina, designed several successful boats for Coronado that were remarkably similar to Lapworth’s Cals.
Perhaps the most successful of the little sisters to the Cal 40 was the Cal 34. The Cal 34 was in production off and on, and in various configurations, from 1966 until 1979.
Although the hull form of the Cal 34 remained basically unchanged during its production life, enough changes were made in the rig, deck molding, and interior for the boat to have three model designations: Cal 34, Cal 2-34, and Cal 3-34.
Sailing Performance
The Cal 34 was conceived as a true racer-cruiser, and early promotional literature stressed her racing performance. The original rig was a low aspect ratio masthead sloop. With a foot length of 14′ and a hoist of 33.5′, the mainsail was of typical late CCA (Cruising Club of America) Rule proportions. The long boom of the original short rig overhangs the cockpit awkwardly, with the mainsheet traveler just forward of the aft end of the cockpit. According to owners, this makes access to the cockpit lockers a nuisance, as well as squandering cockpit space. The tiller occupies the entire forward half of the cockpit, so that the helmsman sits just aft of the deckhouse, while the sail trimmers sit further aft.
The rig on the 2-34 and the 3-34 is just over 2′ taller and the boom 3′ shorter than the original. These dimensions give the rig much more modern proportions, reducing the size of the mainsail by 40 square feet and increasing the aspect ratio of the main from about 2.5:1 to 3.25:1. With the taller rig, the typical PHRF rating of the boat is six seconds per mile faster.
Most Cal 34 owners we surveyed consider the boat to be about the same speed as similar boats upwind, and somewhat faster downwind. This assessment jibes with the performance of most Lapworth designs, which are at their best off the wind. The boat’s PHRF rating, however, suggests that, on the whole, the boat is actually slower than more modern designs of the same size. The C&C 34, for example, is rated about 25 seconds per mile faster than the Cal 3-34.
According to owners, it takes a good breeze to get the Cal 34 moving. With her large, trapezoidal fin keel, the Cal 34 simply has a lot more wetted surface than more modern fin keel boats, although substantially less wetted surface than a full keel design.
Many owners of the original Cal 34 have shortened the foot of the mainsail to improve the boat’s balance. The taller-rigged boats have inherently better balance, since the center of effort of the entire sail plan is further forward. Boats with the short rig and a shortened mainsail foot are likely to be underpowered in light air.
One advantage of the shorter boom is to get rid of the traveler at the aft end of the cockpit. Instead, the traveler is mounted on the bridgedeck, or over the main companionway. While this location would be awkward for racing a tiller-steered boat, it’s good for cruising, since the helmsman could handle the mainsheet as well as the tiller.
One of the most commonly-seen modifications to earlier boats is the installation of wheel steering. This requires relocating the mainsheet on the longerboom boats, but it frees up the space in the cockpit dramatically. The Cal 34 really has a large cockpit, but the tiller and original mainsheet arrangement wasted a huge amount of space. Wheel steering is standard in the 3-34 version of the boat, built in 1976 and later.
Construction
The Cal 34 has a relatively unsophisticated, hand laid-up hull. Owners consider the boat to be above average in strength of hull, deck, and rig. A number of owners report that the main bulkhead tends to delaminate due to leaking chainplates. Since this is potentially a serious structural problem, any Cal 34 should be carefully surveyed for signs of leakage in this area. Be particularly cautious about any boat in which the main bulkhead has been painted out, rather than left varnished: look carefully for water stains around the chainplates.
Other areas to check are the deck around the mast step, and the fiberglass keel molding. Internally ballasted boats such as the Cal 34 frequently suffer damage on the toe of the keel when running aground. The keel molding should not ring hollow when tapped with a mallet, which would indicate a loose ballast casting—a sign that the boat has been run aground hard.
Older Cal boats are not heavily built: their light displacement precludes excess material. Furniture and bulkhead tabbing are relatively light, notoriously so in the old Cal 40. The saying about the Cal 40 is that when the berths pop loose in the forward cabin, it’s time to reduce sail.
Despite fairly light construction, we know of several Cal 34s that have done impressive ocean voyaging. We wouldn’t consider a boat of this age and construction suitable for ocean cruising without a careful survey of all structural components. Lightdisplacement hulls such as that of the Cal 34 get a lot of stiffness from the bonding of furniture to the hull. Keeping it in place is important.
One problem area is the chainplates. Several owners report chainplate failure due to metal fatigue, and one owner found several other partially broken chainplates when he replaced on that had broken.
On the whole, however, the Cal 34 is relatively free of structural defects that would be the result of poor workmanship or choice of materials. The faults you find are more commonly a function of the age of the individual boat. For example, some owners report sloppy rudders due to wear of the fiberglass tube which serves as stuffing box and bearing for the rudder stock—a common aging problem with this type of rudder installation.
Pay particular attention to the condition of the gelcoat, particularly the deck gelcoat. Crazing is very common. Unless it has been painted, the distinctive blue Cal sheerstrake is likely to be badly faded in older boats.
In the late 60’s and early 70’s, many West Coast boats, including Cals, were notorious for mediocre systems installations, particularly wiring and plumbing. If an older Cal 34 has had a lot of electronics added, there’s a good chance that the wiring has been pigtailed onto existing circuits, a poor practice. Older Cal 34s also had gate valves rather than seacocks on through hull fittings. These should be replaced.
Other minor weak points include the lack of backing plates on stanchions, which can cause localized crazing of the deck, and leaking aluminumframed cabin ports.
Owners recommend putting in larger cockpit scuppers. The big cockpit can hold a lot of water, and the two small stock scuppers are inadequate.
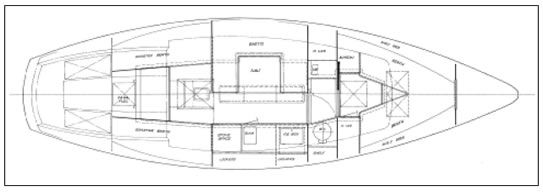
Interior
There have been two interior layouts in the boat. The original Cal 34 and the 2-34 have two quarterberths aft, with the galley to starboard and a dinette to port in the main cabin. The later Cal 3-34s have a more modern conventional layout, with galley aft to port, quarterberth and chart table to starboard. The saloon of the last version has a settee to starboard, dinette to port. Both layouts have V-berths in the forward cabin with the head between the main cabin and forward cabin. Head layout is different in the two models.
On the whole, we think the later layout is superior, although the galley is actually larger in the original version. On older boats, most owners use the dining table for chart work, although it would be quite easy to design a slide-away chart table to fit over the head of one of the quarterberths.
The interior finish of the boats changed a lot over the years. The original Cal 34 had a varnished mahogany plywood interior with varnished mahogany trim. Later boats went to the oiled teak cave look of the 1970s.
There is no doubt that the original interior is lighter and brighter than the later teak interior. However, a varnished mahogany interior requires more upkeep than an oiled teak interior, and is harder to restore to good condition if it has been allowed to deteriorate. Mahogany blackens when exposed to salt water, while teak merely bleaches out and can be reclaimed with a little sanding.
There’s a lot more in the way of creature comforts in the 3-34, in keeping with the growing view that cruising should be more than an expensive form of camping out. Water capacity was increased from the marginal 26 gallons of the early boats to a more serviceable 60 gallons, hot and cold pressure water were standard, and a shower was installed.
The interior is a good selling point in any of the three models. For its length overall, the Cal 34—which is really just over 33′ long—has a lot of interior volume. Headroom on centerline in the main cabin is 6′ 2″. The boat easily has as much interior space as older boats 3′ or more longer.
Engine
Like most boats built in the late ’60s, the Cal 34 was originally powered by the Atomic Four gas engine. The engine is located under the cockpit, but is reasonably accessible from either of the quarterberths.
The propeller is driven through a V-drive, and some owners report problems with this unit. A thorough mechanical survey is a must when buying a Cal 34.
In the mid-’70s, diesel engines made their appearance in the boat. A variety of diesels have been installed, including Farymann, 25 and 30 horsepower Westerbekes, and the Perkins 4-91. We would not buy a boat with a Farymann diesel, since parts are difficult or impossible to find. Oddly enough, the most desirable engine for the boat may be the old Atomic 4, which many owners report to be still running strong at 15 years of age or more. Parts are readily available, and are likely to be for some time to come. You could also consider replacing the Atomic Four with one of the Universal diesels designed as a drop-in replacement for the engine.
One disadvantage of the new version of the interior is that engine accessibility has been sacrificed. Owners consider access fair to poor in the aft galley interior, fair to good in the double quarterberth version.
One oddity is that many owners report that the boat pulls strongly to starboard under power, requiring a lot of helm for correction, while another owner reports that the boat pulls strongly to port with the same engine!
Buying a Used Boat
Early models of the Cal 34 are well over two decades old today. A lot of changes have occurred in the industry in those 25 years, as well as in the expectations we have for medium-sized cruising boats. Certainly a lot of features of the later Cal 34s—the more efficient rig, better sail handling layout, wheel steering, anchor locker, diesel engine, bigger water capacity and other creature comforts, and more useful interior layout—make them more desirable for most uses. Of course, the price of newer boats reflects the improvements.
An older Cal 34 would be a good choice as an entry-level, medium-sized family cruising boat. A lot of the gear on older models will be painfully obsolete. The rigging, sails, and electronics are likely to be old. Unless the boat has been unusually well maintained, the wood cockpit coamings may need replacing, the hull is likely to need painting, and the deck gelcoat will be crazed.
Blistering has been a relatively minor problem with older Cals, but the hull should obviously be carefully surveyed for high moisture content.
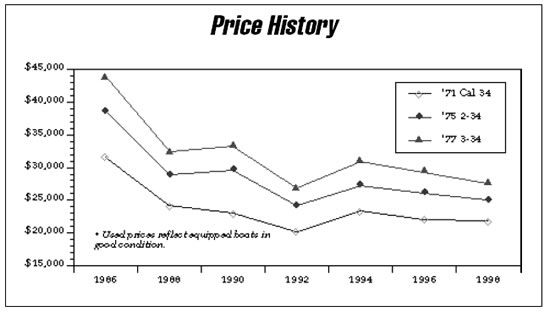
The base price of the Cal 34 in 1969 was $16,800. This was for a stripped boat—the base price didn’t even include lifelines and stanchions.
The next year the base price climbed to $19,277, and it continued to escalate throughout the boat’s production history.
There’s a good chance that an older Cal 34 will give you all the opportunities your heart could ever desire to learn to tinker with fiberglass repairs and the upgrading of systems.
If you’re willing to do this type of stuff yourself, a 20-year-old performance cruiser that you can buy in today’s market for $20,000 or so may be a lot of boat for the money. If you want a lower maintenance boat, stick to a late model Cal 34—but be prepared to pay significantly more.











Lots of useful info even though I’ve had a Cal 2-34 for 25 years ! Better check those chain plates…