Hunter Marine Corp. is noted for its slick, innovative and low-cost mass production sailers. The Hunter 23.5, new in 1992, fits the bill in all respects.

The 23.5 was designed as a trailerable family cruiser for entry-level sailors. Like most Hunters, the boat offers lots of space in the cockpit and down below, and comes with the famous Cruise Pac, which provides just about anything a customer needs, including sails, motor, trailer, lifelines, anchor, life jackets, flares and a copy of Chapman’s Piloting, Seamanship and Small Boat Handling. It’s this type of marketing (plus price: the 1992 price was $13,500) that has helped make Hunter one of the most successful sailboat producers in the U.S.
No one has ever faulted the Alachua, Florida, builder for offering anything but fresh, well-thought out designs. The most striking feature of the 23.5 is its water ballast system, new to Hunter. The system permits an operator to remove 1,000 pounds of ballast from the trailering weight. A retractable centerboard, kick-up rudder and mast that’s fairly easy to step and unstep further enhances trailerability. All told, boat, motor and trailer weigh a combined 2,450 pounds. This model also contains enough foam to provide positive flotation.
While Hunter has enjoyed considerable success with the buying public, it has also suffered from a negative image problem. Earlier PS reviews have criticized Hunter products for a lack of quality control-various systems kinks, lightweight hulls, poor finish work and general absence of blue-water seaworthiness. On the other hand, Hunter owners, while acknowledging a prevailing lack of respect, frequently defend their choice. In the realm of objective data, Coast Guard complaint and recall statistics reveal that Hunter has a better than average record when it comes to hull blistering. (Hunter offers five-year bottom blister warranty protection for the 23.5.) Clearly, the company is doing something right. The model we inspected (hull #8) showed, with very few exceptions, careful attention to detail and finish work in even the least accessible places-more than youd expect on a $13,500 boat. But it is also a boat with some inherent contradictions, in our opinion.
The Boat
The 23.5 is a highly engineered product with lots of thoughtful features. Hunter, unlike some builders, constructs a mock-up, followed by a prototype that is extensively tested before final design decisions are made. The hull form is modern looking, almost powerboaty in appearance from some angles. Continuing a tendency evident in recent Hunters, the design team has given the 23.5 a relatively full hull, and raised the freeboard to reduce the cabin height, as well as add room below and keep those up top dry in a chop. Because the cabin extends to the rail (no side decks), you must climb over the cabin top to get to the foredeck.
The rig (a B&R design) consists of a 28-foot Z. Spar mast, fractionally rigged with swept-back spreaders that eliminate the need for a backstay (and make un-stepping/stepping, hence trailering, simpler); for the most part, the uppers are aft of the “after” lowers-until deck level-creating a triangular support system. Main and jib halyards are internal and led back to the cockpit. Power comes from a fully battenedmainsail and 110-percent jib (UK Sailmakers-Hong Kong) with a total of 236 square feet. For steering, the traditional wooden tiller has been replaced with a brushed aluminum tube that arches over the walk-through transom (swim ladder comes standard). The aluminum, said chief designer Rob Mazza, weathers better and is easier to arch in order to keep the rudder low and the tiller sufficiently high. Many helmsmen will use the standard Ronstan X-10 tiller extension.
The water ballast/keel system constitutes the key feature of the 23.5. The water ballast-125 gallons, or 1,000 pounds-takes about two minutes to bring on board. The system is activated by flipping up a lid at the base of the companionway, opening a vent and turning a T-valve; the valve in turn drops a circular stainless steel plate aft of the keel, exposing four holes in the hull. (The plate can then be closed flush.) And while you can’t jettison the water downwind, you can swing up the centerboard to reduce draft to 18 inches. The 4-foot centerboard, controlled by the outboard line to the cockpit, moves easily up and down via a cascade block and tackle arrangement.
The apparent thinking of Hunter engineers was to provide a simple, one-step water ballast system that keeps draft shallow while lowering the center of gravity for added stability and righting moment. The ballast-about 16 cubic feet in volume-lies immediately below the waterline. When the water is added, the boat sinks several inches. Nevertheless, while the water adds 1,000 pounds to the overall displacement, its location does not seem to provide sufficient righting moment for windward work in gusty conditions. On racing boats, water ballast is carried above the waterline and outboard under the settees, which of course provides more righting moment. But this water must be pumped into the chambers and drained before tacking-too complicated for Hunter’s purposes.
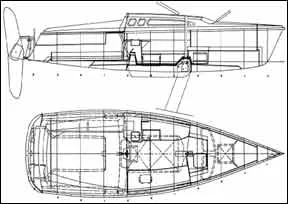
Construction of the boat is fairly straightforward, with balsa in the hull and plywood in the deck. The plywood core has the potential to encourage water migration should a deck leak occur at some point. The deck/hull joint, with a roll similar to a Hobie 18-a “modified shoebox,” one Hunter engineer described it-is bonded with glass and further fastened by flathead screws through the rubrail. Stanchions, fastened to aluminum backing plates that are glassed in, are sturdy. Though not a heavily-built boat, the 23 looks solid enough; in the absence of a graceful hull form-no sheer here-Hunter provides some added dash with a smoked forward-facing window and a green and purple hull swoosh graphic, which apparently has drawn strong reaction, pro and con (We liked it). Oddly, there is no waterline or boot scribed in the hull. Perhaps Hunter anticipates owners dry-sailing the 23.5, but the absence of a waterline mark will make bottom painting a difficult chore the first time.
Performance
We test sailed the 23.5 off Newport, Rhode Island. In light-air conditions, the shallow-body, lightweight boat (displacement 3,000 pounds with the water ballast) moved up to speed quickly. The boat pointed high and the few light puffs we experienced produced no noticeable helm. We did have some problem finding a definitive groove, especially after tacking. The boat glided through the water easily on a reach and downwind, with the board up, sped along as much as a 23-footer can (Mazza said it will surf under the right conditions). We moved relatively faster, in fact, than a Nonsuch 27 on the same tack.
In stronger 15-20 knot winds, it is a whole different experience. With a single reef in the mainsail, the boat consistently rounds up and stalls. In addition to the boat’s higher vertical center of gravity, this tendency may also be due to the very high-aspect ratio centerboard, which is generally associated with quick stall characteristics.
Complicating matters is the way the rig and sheeting are set up. With no backstay (or topping lift) and no traveler, and with the main sheeted down and far forward near the companionway, the main and sheet are highly stressed. And because the cam cleat for the mainsheet is down near the cockpit sole, it’s difficult to reach-especially in heavy air on a beat, when the helmsman and everyone else is out on the rail. The rounding up and stalling require constant spilling of the main. This may be okay (if tiring) for the experienced sailor, but a bit strenuous and nerve-wracking for the beginner at whom this boat is marketed.
Instead of a single reef, one solution might be to take a second reef in the main in anything approaching 15 knots, but that’s not much of a solution. With 236 square feet of sail-128 in the main, 108 in the foretriangle-for a sail area-displacement ratio of 18.9, the boat should not be overpowered. (The O’Day 23, of about the same displacement, but with 200 more pounds of ballast, carries 246 square feet)
Another solution, although it breaks up the cockpit, might be a barney post where there’s already a slot for the cockpit table, a system that worked well enough in the Alerion-Express. A traveler would be even better, though obviously Hunter wanted to keep the cockpit clear of obstructions as well as avoid the added cost.
Accommodations
You get a lot for your money with this Hunter model. One thing you get a lot of is interior space or, as company literature describes it, “a 25-foot boat in a 23.5 hull.” The main cabin is sizable and has more headroom than we’ve seen on a 23-footer. A pop-top hatch allows those down below to stand up in the center of the cabin. An optional canvas camper top ($300) provides protection from the elements. Poptops are notoriously leaky, and we can’t vouch for this one’s water tightness; however, Hunter has provided drains all around.
The smoked pop-top, plus three ports per side in the main cabin (two small circles, one longer swoosh-style forward) and the forward-facing window provide plenty of light. Hunter has made no attempt to yacht-up the interior: What you get is a basic cream-colored liner, offset on a portion of the topsides by a close-weave grayish fabric someone called “monkey fur.” Despite the plainness, we liked the clean look of the interior.
Aft to port in the main cabin you get a galley station with a one-burner alcohol stove, sink, and fold-out table with storage below. You won’t be whipping up any Cruising World-style feasts in this galley, but it’s nice to be able to heat up some coffee or a cup of soup. Forward of the galley is a small settee/berth, sized right for a child, with storage beneath and a cutout for a portable ice chest. Opposite is a somewhat longer settee/berth of less than six feet, with more storage and a battery compartment below. On the centerline is a slot for a small table that also can be set up in the cockpit.
There are a number of helpful additions: an automatic bilge pump, access plates underneath the cockpit winches. The portable toilet is located to starboard behind a half-bulkhead and privacy curtain, and under the V-berth. Aside from the standard V-berth in the bow, which seems a bit cramped, there’s a double berth (plus stowage) aft of the main cabin, under the cockpit and seats (not for the claustrophobic). It was back here in the bowels of the boat that we spotted the only untrimmed fiberglass.
On deck, there’s an equally roomy cockpit-7′ 9″ long and 6′ 2″ from coaming to coaming. The relatively wide beam makes the addition of a ridge along the centerline for use as a footrest a welcome touch. Foam padding on the seatbacks is another. A lazaret on either side provides on-deck stowage. There’s a #8 Barient winch on either side of the cabin top, each with an attendant cleat. Lines are meant to be kept in the no-name stoppers to starboard. Because of the profusion of lines led back on the starboard side, we’d prefer an extra cleat and winch.
Nonskid is molded in. The foredeck holds an anchor locker, which also contains a padeye for the stepping/unstepping operation. Skipping the details of this procedure-which involves use of a gin pole, the main and jib halyards and a bridle that controls lateral movement-we’d say that Hunter has devised as easy a way to drop a mast as is possible. Once down, the forward end rests in a U-shaped bend in the bow pulpit, the aft end on a roller-topped pole fitted at the transom.
Conclusions
In its attempt to create a simply operated, easily trailered, entry-level boat at a good price, Hunter has come up with some clever compromises. But they are compromises just the same. The 23.5 sails well on all points in light air; it does well off the wind in heavier air. Windward work over 15 knots in this boat is poor in our estimation. We’d strongly recommend that potential customers thoroughly test sail the boat in a variety of wind conditions, experimenting with one or two reefs, to be certain it’s something they’re able-and willing-to handle.
The Hunter 23.5 is clearly striking a chord with some buyers, and assuming many are entry-level sailors, we think it’s great that this boat is attracting newcomers to the sport. The design represents a clever way of managing the trailering problem (i.e., weight and draft). At the same time, we can’t help but wonder if its behavior in gusty winds is worth the convenience of dumping ballast on the launch ramp.











excellent article.
Thank you.
Darrell – excellent review. Thanks.
Rob Hughes
Thanks for the review, I just saw one for sale online.