Back in 1965, a St. Petersburg, Florida sailmaker named Charlie Morgan, who had been dab bling with custom racing yacht design and had come up with a remarkable string of winners, started producing a series of small- to medium-sized production boats. Introduced late that year, the Morgan 24 joined the Morgan 30, 34 and 38, becoming an instant success as a fast cruiser and club racer.

Morgan 24/25 specifications
In 1968 the Morgan Yacht Corporation was bought by the conglomerate, Beatrice Foods, and by early 1969 the Morgan 24 had been renamed the Morgan 25, with some changes in specifications and options. For example, although the actual length overall remained at 24′ 11-3/4″, the advertised length moved from 24′ 11″ to 25′ 0″; inboard diesel and gasoline engine options were offered in addition to outboard power; toerails switched from teak to molded fiberglass; and the transom outboard cutout was eliminated in favor of an optional outboard bracket.
Morgan Yachts was later resold to Thor Industries and most recently to Catalina Yachts. After about 1972 more changes were made. The hull-deck connection went from through-bolted to pop-riveted; rigging blocks were downsized; window frames were changed from silver anodized aluminum to black plastic; the water tank changed from stainless steel (Monel in the early boats) to galvanized. The last Morgan 25s were built in 1976. Over the years, between 400 and 500 were built.
Design
The Morgan 24/25s long waterline, very well balanced hull, relatively low wetted surface, large sailplan (for its vintage), and attention to small details like well-shaped foil blades and flush-faced through-hulls, provide good speed and close-winded sailing for the racer. At the same time, its shallow draft (2′ 9″ board up) and relatively roomy layout below appeal to the cruising sailor.
The boat has firm bilges to help with form stability, and a reasonable 5,000 pounds of displacement. However, with ballast placed relatively high due to the shallowness of its keel, the Morgan 24/25 is a bit on the tender side in heavy air.
On Deck
The cockpit is eight feet long, but underway it comfortably seats just two on each side of a long (4-1/2′) low tiller that extends within 22 inches of the companionway. In a race, the third and fourth crew, if any, have to move from cockpit to cabintop, due to crowding and because the boat tends to get stern-heavy with crew weight aft. Because of this, serious racers tend to remove the outboard engine from the transom and stow it below, if rules permit.
The cockpit sole slopes aft to a single centerline scupper through the transom, and this works satisfactorily except for a puddle of water that gathers on the leeward side in rain, and except for the smallish scupper size (1-1/4″ diameter), which some owners have enlarged for faster drainage.
The base M/24 was offered as a relatively bare cruising version, with small (#2) South Coast sheet winches, end-boom sheeting without a traveler, short genoa tracks along the toerails, and no spinnaker gear. An extra-cost optional racing package included spinnaker gear, #3 genoa winches, longer genoa track, six extra cleats, two extra genoa cars, boom vang, snatch blocks, and traveler. Other extras included stainless bow pulpit, lifelines and stanchions, interior and running lights, and compass. The factory-installed options were fairly expensive, with the result that many sailors bought the base version and added equipment themselves. That, plus the fact that M/24s were available at one point as kits, may account for the wide variation in quality, style, and placement of equipment.
Construction
As one owner puts it, only slightly mixing metaphors, The Morgan is a Chevrolet, not a Hinckley. For the most part, owners mention defects in passing but on the whole are very satisfied. One says his forward V-berth bulkhead came loose and had to be refastened, but also reports that fiberglass work is generally neat and strong.

Most boats came off the line with faucet-type gate valves on the through-hulls; many owners report replacing them with more suitable barrel or ball valves.
On the older 24s with teak toerails, the deck is fastened to the hull along a wide L-shaped flange with 1/4-inch stainless bolts on 2-inch centers, with every other bolt passing through both teak and fiberglass-a very strong arrangement. But on the newer
25s, the teak rail was eliminated and the joint fastened with pop rivets, a weaker system that is more likely to leak.
Common problems on both 24s and 25s include leaky windows and crazed Plexiglas; a mast hinge that is virtually useless due to lack of provision for preventing side sway when lowering or raising the mast; dissatisfaction with the dated appearance of the simulated wood-grain mica bulkhead finish, which requires major effort to remove and replace; and centerboard difficulties.
The centerboard pennant arrangement is probably the weakest design detail on the boat. The board itself is a well-shaped, high-aspect ratio, solid fiberglass unit in a trunk beneath the cabin sole. The 1/8-inch stainless steel pennant wire attaches at one end of a groove molded into the top of the board, winds its way via a stainless steel piston through a stuffing box to a turning sheave forward, then through two more sheaves an to a small winch mounted on the cockpit wall. Several problems can arise due to this design. The lower portion of the pennant, being exposed to seawater, tends to corrode rapidly, and is impossible to inspect without complete disassembly. Hence frequent inspection, requiring a haul-out or scuba gear, is advised. In southern waters, some pennants have failed in less than a year of service. Additionally, several owners report trouble with cracking and leaking in the short stub of hose that bridges the stuffing box and trunk. And unless the owner adds stops at both its ends, the piston can part company with the stuffing box and possibly sink the boat.
Other centerboard-related problems: The turning sheave, under the sole forward of the trunk, is almost inaccessible; owners are well advised to cut an access hole and lubricate the sheave frequently to minimize corrosion. And on some boards, insufficient glass reinforcement around the pin can result in eventual cracking or breakage of the board at the pin hole.
Interior
The 24s and 25s at various times were made with two different interior arrangements: (1) a dinette model with a single sail locker to port, and (2) a two-quarterberth model with twin sail lockers. The dinette version has less space for sail stowage, and there is a considerable amount of wasted space under the starboard cockpit seat unless an access hole is cut in the plywood bulkhead aft of the quarterberth (which is often done). For cruising, however, the dinette model wins hands down, given the greater storage space in the galley and a hanging locker, better privacy inherent in the position of the offset head, and a sizable table for dining or laying out charts. Sitting at the dinette is uncomfortable for four people due to the deck overhanging the outboard seats. In all, most agree that the 24/25 is really a two-sleeper, two-eater vessel.
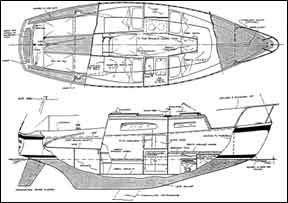
Morgan 24/25 Plans
Still, the boat has practically all the interior conveniences one could want in a small cruiser, including galley, sink, ice chest, marine toilet in a private compartment, good sized berths, long self-bailing cockpit with at least one sail locker, and 5′ 8″ headroom.
The sixtyish interior aesthetics are not great and vary with model year. In 1965 the Morgan brochure says mahogany interior trim but by 1967 the standard interior was bulkheads… paneled in woodgrained mica, with oiled American Walnut trim. Carpeted cabin sole was standard, with a teak sole optional.
A common complaint among owners is that there is no good place to store a portable gas tank. The usual place is in the cabin, aft of the companionway ladder, but that can be a source of annoying-and dangerous-fumes. A 6-gallon tank can be wedged between the cockpit seats, but limits footroom and movement around the cockpit, and the extra weight in the cockpit does nothing to help performance.
Other complaints include the fact that the icebox drain runs into the bilge, providing a source of potential odors; and that ventilation is only so-so. A cowl vent fitted on the foredeck, plus a mushroom vent over the forward hatch, are recommended additions.
Performance
The long, deep board helps the 24/25 to point high, and its low wetted surface, especially with board up, gives extra speed on reaches and runs. The boat performs best in 5 to 15 knots of breeze, but can handle much higher winds when properly reefed, though several owners reported that the boat could be a bit stiffer.
The 24/25 is unusually well balanced, and in ordinary weather can be made to self-steer on a beat or close reach with tiller lashed. However, in very heavy air carrying a chute, it has a marked tendency to broach.
A typical PHRF rating is 219, compared to a J/24 at 171 and a Cape Dory 25 at 261.
Conclusion
Pride of ownership seems particularly evident among owners of the early M/24s, who tend to turn up their noses at the later M/25 as a less sturdy and well-appointed boat. Over the years, both models, and particularly kit boats, are likely to have had major changes to equipment and rigging, some good, some bad. Consequently, prospective buyers should check to be sure any such modifications are appropriate, and should keep in mind that these boats are now 18 to 28 years old, so should be closely inspected for gear that can fail due to aging. Most such gear is repairable, but at a cost. Still, if you find one on which extensive work isn’t necessary, it can be a real bargain as well as a real pleasure to own and use.
In 1972 the Morgan 25 had a base price of $7,495. Earlier models in reasonable condition can be had today for about $5,000, more depending on sail inventories end equipment. Inboard models of the 25 are higher yet, though we feel the outboard model is a better choice.
The Morgan 24/25 makes a wonderful small cruiser and club racer, and can be a solid value if you buy the right boat. Construction quality has varied over the years, and so has quality and quantity of equipment purchased by individual owners. Moreover, all 24s and 25s, even the good ones, are beginning to show their age. Buyers are advised to make a careful inspection to be sure they’re not getting a boat with more problems than they care to handle.










