The Tartan Ten was born out of a popular rebellion against the international Offshore Rule (IOR) in the mid 1970s. This was the worst period in the IOR’s history, when production sailboats were outdesigned even before their molds were finished. Although the IOR has since then gotten its act together, a great many of its early proponents had been lost for good by 1979. The disenchanted went in two directions—PHRF and offshore one-design.
The Tartan Ten is the child of Charlie Britton of Tartan Marine. Britton was one of the first to recognize the market for offshore one-designs. While he was conceptualizing the Tartan Ten, the J/24—soon to become the most successful offshore one-design—was being tooled up for production, although Britton didn’t know it was on the horizon. He was impressed by the Danish-built Aphrodite 101. It’s no coincidence that the Tartan Ten bears a resemblance to some of her features. Sparkman and Stevens designed the boat for Tartan in 1977; production began in early 1978, and ran through 1989.
Most of the boats built went to sailors on the Great Lakes, and most of them spend most of their time racing one-design. There are several hundred boats in the national class association, and the majority of those members race in one-design fleets on Lake Erie and Lake Michigan. According to class officials, there is one-design racing every weekend on Lake Erie, and small fleets in Long Island Sound, Chesapeake Bay, Houston and Jacksonville. Unlike a great many boats that tout themselves as offshore one designs, the Tartan Ten is one of the few boats that has accumulated enough numbers to actually race as a one-design.
When the Tartan Ten was introduced in 1978 at a base price of $21,500, she sold easily. Several boats a week were produced in the years immediately following. Then a steady series of price increases, the recession of 1981 and the first signs of a saturated market began to take their toll on sales. For Charlie Britton, a boatbuilder first and a businessman second, the problems of running so large a business was more than he wished to handle. So in the spring of 1982, production of the Tartan Ten ceased and Britton put his company up for sale. By the spring of 1983 he found a buyer in John Richards and production began again at the rate of two Tartan Tens a month.
Construction
While we wouldn’t consider the Tartan Ten to be one of the better-built racers, she doesn’t have to be. Since she is primarily intended to race against her sisters, consistency between boats is perhaps more important than superior (and hence, more expensive) construction. The major construction criterion she must meet is to be sufficiently seaworthy to endure an occasional short offshore race. She meets this criterion, although, like too many production boats, she barely makes it.
There have been a number of problems with the Tartan Ten over the years. Tartan Marine generally acted responsibly in correcting them. The worst problems occurred in the first 100 boats. For example, the original hollow stainless steel rudder posts were too light and bent too easily. According to Tartan, every boat with that type of rudder post was located and repaired by inserting a second post inside the original one.
A second problem was with the reinforcement of the hull around the keel sump and under the mast step. From 5′ forward of the transom, the Tartan Ten’s hull is cored with 1/2″ balsa, except in the bilge area, which is stiffened by a grid of hollow, hatshaped fiberglass floors and stringers. Because the Tartan Ten has a relatively flat underbody and fin keel, she is more susceptible to flexing of the bilges than a boat with deeper, more rounded bilges.
In the first 90 boats, the grid was neither stiff enough nor attached to the hull securely enough to prevent flexing. As a result the fiberglass tabbing which holds the grid to the hull began peeling off. On a few boats, small cracks developed in the grid and in the bilges. Tartan claimed that it sent repairmen all around this country to track down and fix every boat earlier than hull #84. In most cases the repair consisted of removing the old tabbing and re-tabbing with a heavier laminate. In cases where the grid or hull actually showed damage, more substantial repairs were made. According to Britton, “We got every one of them.”
The mast step has been strengthened several times during the Tartan Ten’s history. The Tartan Ten has a deck-stepped mast, rare in non-trailerable racers, because they offer less control of mast bend. They are no less seaworthy than a keel-stepped mast, provided there is adequate support underneath the mast, such as a compression post or bulkhead in the cabin.
The Tartan Ten’s compression post sits on top of the floor grid. After the initial problems with the first 83 boats, a 5″x4″x1/4″ aluminum plate was used under the compression post to distribute the load. The thickness of the aluminum plate was later increased to 1/2″. Mast step problems still existed to some degree after the first 83 boats. On a hull numbered in the 150s, we observed that the compression post had been moved off the floor grid (presumably because it was crushing it) and lengthened with a threaded extension so it rested directly on the hull.
Unlike most boats, which have shroud chainplates which extend above deck, the Tartan Ten’s shrouds pass through the deck to chainplates in the cabin. Although this may reduce windage and genoa chafe, the hole in the deck is difficult to seal. Many owners report chronic deck leaks around the shrouds.
The chainplates are anchored on a heavy fiberglass “tab” which extends up from the topsides inside the main cabin. According to the manufacturer, there were two chainplate tab delaminations in the first 100 boats. Tartan attributes this to the hull being cored under the tab. Tartan didn’t take steps to correct the potential problem until nearly 100 boats later. One owner of a 150-series boat reported that he had reglassed one chainplate tab after he noticed the telltale signs of delamination—the color of the tab changing from dark green to white where it is anchored to the hull.
By hull #200 Tartan had eliminated the core under the tab and began anchoring it directly to the outer skin of the hull. This didn’t completely solve the problem, according to Britton. Because the section of the topsides around the chainplates was uncored, that section could dimple inward slightly under heavy rig loads, causing isolated incidences of gelcoat blistering and delamination. Tartan corrected this problem shortly afterward—”about hull #270,” according to Britton, by widening the chainplate tab from 12″ to 18″.
Although the Tartan Ten is cored through 80% of her hull, she exhibits a fair amount of structural flexing. As one successful Tartan dealer pointed out, “she’s not overbuilt like the rest of the Tartan line.” We had several reports of the cockpit flexing noticeably while sailing in rough weather. Part of the reason is that the bulkheads under each side of the cockpit are glassed firmly to the hull, but very poorly attached to the cockpit seats. Also the main bulkhead is well forward of the mast and divided by the forward berth. A bulkhead in two halves located away from the chainplates is not very effective in absorbing rig loads. Instead the hull will flex.
The Tartan Ten’s hull-to-deck joint consists of an inward turned hull flange overlapped by the deck and topped by an aluminum toerail. The hull-to-deck joint is bedded with butyl tape, which stays soft and rubber-like for the life of the boat. It has no adhesive properties, but is a good watertight sealant. We have seen it melt and “bleed” out of hull-to-deck joints on occasion.
A strip of aluminum is glassed under the hull flange. This allows Tartan to fasten the hull and deck with bolts, but without nuts, by tapping the bolts through the aluminum insert—a real time saver. The bolts must be bedded, though, or corrosion would compromise the integrity of the joint, especially important since there is no chemical bond to fall back on. Tartan beds the bolts with silicone, which is probably adequate, but a chromate paste would be a better (although more expensive) bedding material. The hull laminate was strengthened when production was into hulls numbered in the early 100s. A heavier mat was added to improve the bond between the balsa core and the laminate. An extra layer of fiberglass was added to the hull laminate as well.
Rig
The mast of the Tartan Ten is a “safe” section. It bends easily with the backstay, but is sufficiently strong to sail without running backstays in a strong breeze. The shrouds are swept back.
The mast is not anodized. On early boats, it was finished with clear lacquer; later it was painted black. According to Frank Colaneri of Bay Sailing Equipment, who rigged all Tartan Ten masts until the mid-’80s, finishing with lacquer or paint is cheaper than anodizing.
On the first 150 or so boats the jib and spinnaker halyards are both wire and exit the mast above the hounds. They then lead through “bullseye” fairleads which have a tendency to chew the wire. (Colaneri called them “wireeaters.”) This system was redesigned so that now the wire jib halyard exits below the mast without a fairlead, and the spinnaker halyard, still exiting above the hounds, was changed to rope.
Schaefer booms were used on the first 70 boats, and bent reefing hooks were a problem. Since then Tartan has used Kenyon booms. The Kenyon booms have no outhaul car, instead relying on clew slugs to support leech tension. According to Colaneri, many booms had to be retrofitted with stainless plates over the sail slot because the clew slugs had pulled through the slot.
Handling Under Power
After hull #309 the Tartan Ten was equipped with an 11 hp Universal diesel. Before then a Farymann 7.5 hp diesel was standard. On boats prior to hull #200, excessive vibration and shaft coupling failures were a problem. According to Britton, the cause was poor shaft alignment. Britton says flexible shaft couplings were used on the first 200 boats, because Tartan was afraid the boat would bend under rig tension. The use of flexible couplings meant less attention was paid to alignment—hence occasional coupling failure and excessive vibration. Solid couplings were used on subsequent boats. “We thought we were bending the boat (by tensioning the rig), but we were wrong. Now we know it’s better to concentrate on alignment and use solid shaft couplings,” says Britton.
Because vibration could be a problem, when considering a used Tartan Ten you should check both the engine mounts and the electrical harness on the back of the engine. The covering of any wires attached to the engine should be checked for wear.
Tartan Ten owners report that the Farymann is relatively trouble free, runs well and is easy to hand start should the battery run down. Owners also say it tends to be underpowered. “Doesn’t do well into the wind,” reported one owner. A folding prop is standard equipment.
Access to the engine is excellent. The fiberglass engine box is light and lifts off easily and, because it also doubles as the companionway step, slides forward without obstruction. The box is easy to refit and latch in place. With the box off, all engine parts are accessible.
Handling Under Sail
Tartan Ten owners rave about performance. She may not be a ULDB, but she’s fast for a 33-footer. Typical comments are “Offwind we pass 36′ masthead rigs,” “rides waves well; good control downwind,” and “recorded 15.2 knots, sustained 10.5 knots.”
However, owners do not rave about her handicap ratings. The Tartan Ten was not designed to fit any handicapping rule. She carries an astronomical IOR rating of about 28.5. Under PHRF she rates from 123 to 132, depending on the handicapper. Most PHRF fleets assume that you have a 155% genoa, and the most common rating is 126. Some fleets, such as Detroit, allow the Tartan Ten to sail with its one-design inventory (100% jib) at a rating several seconds slower.
Owners report that she will sail to a rating of 126 in light air with a 155% genoa. However, with her narrow beam, she is tender and becomes overpowered quickly. In winds over 12 knots, she has difficulty winning with a rating of 126. Using a one-design inventory, the Tartan Ten will sail to a rating of 132 in medium winds. Although she is always fast downwind, owners say she has a difficult time making up what she loses upwind in a strong breeze.
Those who want to race both one-design and PHRF have several problems. Until 1982 headfoils were illegal for class racing. The class has dropped this rule to encourage Tartan Ten owners to race PHRF. Running backstays are still illegal for class racing. Although they’re not necessary to keep the spar in the boat, backstays nonetheless will improve performance slightly without rating penalty. Another, more subtle problem, is that a sailmaker will design the working sails of a class inventory differently than he would for a larger inventory. For example, a 100% jib that must be used for both light and heavy air in one-design racing will be a lot more powerful than a 100% jib for a larger PHRF inventory.
Despite its drawbacks the Tartan Ten still makes for enjoyable PHRF racing because its sailplan is so manageable, the boat is so maneuverable, and its cockpit is so easy to work in. It’s hard to believe you’re on a 33′ when you’re racing one; the boat feels much smaller.
As good as PHRF racing can be, one-design racing is even better. Owners report that all boats are extremely well-matched. In this year’s 40′ national championship, the second and third place teams sailed borrowed boats—boats that had not done well in previous regattas. Tartan Ten sailors may push their boats hard, but as a whole they don’t push them hard enough to cause major gear failures. We have no doubt that a hot SORC team could rip a Tartan Ten apart, but for its purpose the boat is well suited.
Before each boat leaves the factory, it is placed in an outdoor pool, and 50-100 lbs of lead is glassed to the hull 5′ forward of the mast to make her float on her lines. Flotation marks are molded into the hull to insure that the lead is not subsequently moved to change the boat’s trim. This helps make the boats equal in performance.
The keels are relatively fair from the factory, although most racers will want to spend a weekend making them smoother.
Most Tartan Tens race with a crew of 5-8. Although she is a light boat, her narrow beam limits the effectiveness of crew weight. Unlike beamier counterparts, such as the J/30, packing on more crew in a strong breeze is not essential. For best performance, the backstay and traveler must be constantly adjusted. Some of the more successful racers routinely barber-haul the jib outboard in strong puffs. As with any light displacement boat, you must be quick on sail trim to keep her level and driving.
Deck Layout
The Tartan Ten is equipped with a tiller, as any boat this small and light should be. With a tiller, though, you need a larger cockpit. The cockpit of the Tartan Ten is 9 1/2′ long, which gives the crew plenty of room for racing. The companionway, though, is obstructed by long stainless steel handrails. When tacking, the crew must all pass through the cockpit.
The cockpit seats have short, outward-angled seatbacks with a small coaming. This provides a modicum of day sailing comfort without sacrificing much racing efficiency. The slotted aluminum toerail does, however, compromise racing comfort. The crew could slide farther outboard for more hiking leverage if it weren’t for the toerail painfully biting into the backs of their thighs. Owners report that the cockpit drains quickly when pooped by a large wave. It nevertheless is worrisome, because its large volume would hold a lot of water, and its 6″ companionway sill would do little to keep that water from rushing below. We wouldn’t race it in rough weather without all companionway drop boards locked in place.
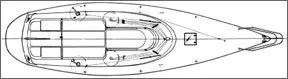
The rudder post exits the deck through a cockpit coaming that wraps around the stern. A tiller is attached to the post; when lifted and lashed to the backstay it leaves the cockpit unobstructed for an extraordinary amount of cockpit space at the mooring. The mast is stepped into a cast aluminum collar on deck. The collar is not hinged. The running rigging exits through the bottom of the mast, then runs through sheaves built into the collar and aft through sheet stoppers to Lewmar 16 winches on each side of the cabin house. Several owners said they had moved or replaced the stoppers made by Delta.
The primary winches are Lewmar 30s. Secondary winches are permitted under class rules, but are not offered as a factory option. Some owners report that larger primary winches are helpful to trim the genoas used for handicap racing. On the boat we sailed, the sheet tracks were backed with strips of aluminum, but the backing plates for the winches were 1/8″ plywood.
The deck gelcoat provides good traction, but this also makes it more difficult to clean. Stanchion bases, made for Tartan by High Seas, bolt through the deck and through the toerail. On the boat we examined there were no backing plates on the throughdeck stanchion bolts, but bolting through the toerail gives the installation adequate rigidity. Several owners reported that the welded sockets for the stanchions have failed.
The boom vang runs in a single part up from the mast step to the boom, then forward to the gooseneck, down to the deck via a 6:1 purchase, and aft to a winch. At the gooseneck, it attaches to a small welded eye, which could be of heavier gauge.
The backstay is split with a 4:1 purchase deadended on the stem. A crewmember would have to sit aft of the helmsman to play the backstay. The ball bearing traveler spans the cockpit and is easily adjusted with its 3:1 purchase. The 5:1 mainsheet deadends on the traveler car.
Belowdecks
For a 33-footer, there isn’t much to the Tartan Ten’s interior. Headroom is only 5′ 2″. However, the companionway hatch is in three pieces and lifts off for stowage below, opening a 5′ long “skylight” in the cabin. This feature provides some amount of standing headroom below, without having to sacrifice the clean lines of the deck to a high cabin trunk. Erecting a dodger over the companionway encloses the standing headroom. The hatch cover could be stronger: we nearly cracked it by stepping on it.
There is no icebox in the cabin. A portable cooler stores in one of the two cockpit lazarettes. The standard head is a portable, stowed under the forward V-berth. Nearly every owner we talked to complained of its smell and said that it is difficult to empty. Most had either discarded it for a cedar bucket or installed a full marine head. There is no built-in stove and the chart table is small.
There is a small sink with a hand pump on the port side. On boats prior to hull #200, the water tank was installed under the starboard quarterberth, with the fuel tank under the port quarterberth. With the water tank and sink on opposite sides, all the water in the tank would drain out through the sink on port tack. Tartan’s retrofit was a rubber plug for the sink nozzle. By hulls numbered in the early 200s, they had switched the position of the fuel and water tanks, solving the problem.
The interior of the Tartan Ten is dark. The bulkheads, cabinetry and cabin sole are teak-veneered plywood. We would paint the settees white. The forward V-berth is a comfortable 6′ long. The “filler,” or section of the berth that covers the Porta Potti is removable for access to the head. However, the filler sits on very narrow cleats, so when you climb over it to get out of the berth, the filler frequently falls off its cleats and you tumble onto the head (Ugh!).
Vertical posts from the overhead to both the sink and the nav station make good handrails for moving about below in a seaway. Under both the sink and nav station are small lockers with zippered cloth coverings instead of doors. There is further stowage under the main berths and quarter berths. These stowage bins are not insulated from the hull, but because the boat is cored, condensation should be minimal. The bins are sealed from the shallow sump if they weren’t sealed, any water in the bilge would predictably soak their contents. One owner commented, “There should have been no attempt to create six berths at the expense of adequate storage.”
On the boat we sailed the joinerwork and furniture tabbing were mediocre. The overhead panels were sloppily fitted. The ceiling is covered with a padded vinyl liner. A strip of wood covers the hullto-deck joint.
There were several major changes to the interior after hull #160. In earlier boats, both the main berths and quarterberths were “root” berths. Root berths are somewhat like pipe berths. They consist of cloth anchored to the side of the hull and slung to a pipe running the length of the berth. The pipe fits into notches so that the angle of the berth can be adjusted to suit the boat’s angle of heel. Another piece of cloth attaches with Velcro to the pipe to form a seat back. While the root berth makes for comfortable sleeping underway, it is far less comfortable than a fixed berth to sit in while the boat is anchored.
After hull #160, the root berths in the main cabin were abandoned for fixed berths, with a dual purpose design backrest/leeboard. Additional stowage bins were added over the main berths. A drop leaf table was also added between the main berths. It is doubtful whether it would survive the rough and tumble of hard racing. We suspect most owners remove it for racing.
Conclusions
Like any boat, the Tartan Ten is built to a price for a particular purpose. She is not built as well, nor laid out as lavishly as, say a J/30; but she is also much less expensive. People don’t buy Tartan Tens to make long offshore passages, nor do they buy them for extended cruising. People buy them to day race, either as a one-design or under a handicap rule. Maybe they throw in an occasional weekend cruise.
The Tartan Ten is a joy to day race. It is easy to maneuver and crew on, offers lively performance, and is affordable. We think that one-design racing would be far more fun than handicap racing. At least under one-design you are competitive in all wind velocities.
The Tartan Ten class association appears to be well organized, which should help keep the resale value of the boat high. If you live near a Tartan Ten fleet, you should give offshore one-design racing a try. But beware; you might get hooked.











