In the late 80’s, the landscape was littered with the remains of boatbuilding companies that couldn’t cut to fit. The conventional wisdom was that starting a new company was guaranteed to convert a large fortune to a small one. In this period, Jeff Canepa conceived the idea of entering the fracas with a pint-sized company based in Santa Cruz, California, that would introduce yet another performance 21-footer.

Canepa is the antithesis of the traditional boatbuilder, staid types who worked their way up the professional ladder by lofting lines, stoking steam boxes and laying planks. Rather, he is an experienced multihull sailor and marketing expert who envisioned catamaran performance in a monohull, identified an existing design that might do it, then assembled a team of experienced designers and builders to develop the final product. The result is the Ultimate 20, a boat finding great acceptance among a group of mid-level sailors seeking new levels of performance, and experienced sailors looking for big kicks on smaller boats. It also appeals to the budget-conscious shopper.
A college dropout with a penchant for water sports, Canepa began sailing in 1968 when he abandoned the classroom during sunny Monterey Bay afternoons and practiced sailing a Hobie Cat. By 1972, he’d captured the Hobie National Championships, followed in 1973 with the first of two World Championships. He then headed for Europe to conduct Hobie clinics until the late 70’s, then expanded his knowledge of the small-boat industry while working to introduce O’Neil Wetsuits to the international sailing community. He furthered his knowledge of the watersports market while setting up an American distribution system for a German sailboard manufacturer.
The first seeds of the U20 project were planted in 1986 when he crossed paths with Doug Hemphill, designer of the Hotfoot 20 and Hotfoot 27, reliable performance sloops built and sailed primarily in Canada. At the time, Hemphill was experimenting with the addition to the 20-footer of a bowsprit, asymmetrical spinnaker, and hiking racks. In 1988, with the sailboat market headed for what the Federal Reserve Board calls a hard landing, he purchased the molds for the Hotfoot 20 at a sheriff’s auction and placed them in a storage container.
“We were way ahead of our time,” he said, “hoping for a recovery. There had been too much money in the marketplace during the 80’s, but we felt that after a few years of cooling it would rebound, and that a niche in the small boat market would be strong.”
By early 1993, he was beginning to look like a soothsayer. J-Boats had successfully introduced a line of “sprit boats,” the Melges 24 was a big spot on the horizon, and trailerable boats were again making their presence felt. With that as a backdrop, Canepa formed Ultimate Sailboats International and began assembling his design and construction team.
For openers, he recruited Ron Moore, the well known Santa Cruz boatbuilder who carved a reputation building the Moore 24 and other ultra-light, ultra-fast boats, giving him responsibility for construction of a prototype, using the Hotfoot molds. Business associate John McWaid was enlisted to hitch the prototype to his car and head into the American hinterland.
The Design
Upon McWaid’s return, armed with input from sailors and sailmakers at all levels of the sport, a year long tweaking process began when naval architect Jim Antrim was commissioned to begin a massive overhaul of the design. Antrim’s recent successes include work as a member of the structural design team for Bill Koch’s America’s Cup winner, and the design of Aotea, a trimaran that recently set a record in the San Francisco-Hawaii single-handed race.
The designer’s first suggestion was to remove the transom and stretch the boat 9″ to 20′ 10″, without making radical changes to the basic hull shape—a fairly flat bottom that tapers out and up to a curved hull-deck flange. Freeboard was increased 2″ and the beam was increased to 8′ 6″, changes that improved the appearance while increasing leg room in the cockpit and sitting room belowdecks.
His next step was to increase the horsepower of the fractional rig by raising the mast height to 30′ above deck level, and eliminating the need for a permanent backstay by adding spreaders swept back 25 degrees. The changes increased the size of the full-roach, loose-footed mainsail to 205 square feet. A working jib carrying 100 square feet of sail is mounted on a Harken roller furler recessed below the deck.
Antrim redesigned the chord of the keel and added a flared bulb that resembles the whale’s tail design seen on many Cup boats. The keel was also moved aft 8″, resulting in an increase in forward buoyancy and improvements in trim and balance, making crew positioning less critical when attempting to maximize performance.
Because of built-in safety features, Antrim is especially pleased with the bowsprit arrangement. Like most, it is launched by pulling lines led aft from the pole tip to the cockpit, which is where similarities end. Most are housed belowdecks and launched through sealed through-hull fittings. By comparison, the U20’s is housed on deck in a molded slot and held in place by a fiberglass cover that is secured to the deck by six screws. So, while operation of the pole is similar to other boats, Antrim feels his design has two safety advantages: In the event of a collision, the sprit or housing will break under 1,700 pounds of pressure, before the hull is fractured; and, in the event the pole breaks the boat won’t be swamped. A deck-mounted pole also increases the amount of interior space, a consideration on any 21-footer. We tend to agree with his assessment, but this arrangement does detract from the overall appearance of the boat. As an alternative, sailors who wish to fly symmetrical chutes can tack the pole to the mast.
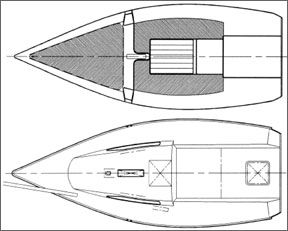
The modified design also incorporates the addition of curves and radiuses to the coachroof and cockpit, subtle changes that softened the edges to improve both appearance and ergonomics. The designer then reorganized the deck layout, and the result is a model of efficiency, enhanced by roller furling and the sprit/asymmetrical chute arrangement. Halyards are internal, led to cleats on the coachroof, so the only lines in the cockpit are main, jib and spinnaker sheets, a single roller furler control, and a line connected to the bowsprit.
Increasing the beam and length increased the cockpit width to 4′ and length to 7′ 8″, providing plenty of room for a typical crew of three, or four when sailing in heavy winds. Sailed with a crew of three, the driver steers from the aftermost position and controls the mainsheet, which attaches to Harken track and a swivel block recessed in the cabin sole. This leaves the trimmers with enough room to perform their tasks forward in the cockpit.
The rudder is a lightweight blade constructed of carbon fiber with fiberglass and wood reinforcement at the head, transom-mounted on pintles and gudgeons that appear to be adequate for the loads developed. By the time Antrim completed the remodeling, the rudder was about all that was left of the prototype.
Construction
Since he has 26 years of experience constructing performance boats designed to sail in rugged conditions, the selection of Moore as the builder was a propitious choice. Though found sailing primarily on the West Coast, his Moore 24 is a seasoned MORA winner, a sturdy boat that holds up well under the punishing conditions found in Pacific waters outside the Golden Gate and along the California coast.
The hull lay-up for the U20 is fairly straightforward, consisting of a 3/8″ core of Baltek balsa, to which 12-ounce layers of bi-directional woven roving knitted in 90-degree angles are applied on interior and exterior surfaces. The final exterior layer is .75 ounce mat. Hydrex vinylester resins are used on exterior skins, and Polyester C2849 on other layers. The deck also is constructed with a Baltek core, over which a 10-ounce layer of cloth is laid, followed by a .75-ounce mat. To enhance the structural integrity of the hull and deck at stress points, two 12″-wide panels of carbon fiber are laid under the keel area and across the width of the deck at the mast step and chainplates. The exterior surface of the hull is a smooth gelcoat surface, the interior a polyester enamel.
Composition of the cockpit sole is identical to the deck, except the core is 3/4″ Baltek.
The hull and deck are bonded with a syntactic slurry of polyester putty, mill fibers and microballoons. Since the deck joint overlaps an eggshell-shaped hull flange that is approximately 2″ wide, both the designer and builder are confident of the structural integrity of the bond, and feel that fasteners would be redundant. Unfortunately, because the joint is exposed, it detracts modestly from the appearance of the vessel and would seem to be vulnerable to collisions.
The bulb keel is raised and lowered by a patent- pending winch assembly that is removable. It can be locked in place by hand with six “Scotty” screws. Canepa said he was considering redesigning the locking device because some owners were shortcutting the procedure by only using four screws. The plate and keel box are fit to the foil with clearance allowed for impact.
Interior
Though the mast compression post and trunk for the lifting keel reduce space belowdecks, we didn’t find the U20 to be significantly less spacious or comfortable than similarly sized boats with fixed keels or centerboards, though quarters are reduced by the long cockpit. Surfaces are smooth, edges are rounded, and a bright white finish creates the illusion of spaciousness.
The forward V-berth is 94″ long, tapering to a 64″ width at the mid-section of the boat, which is functional as a large stowage space, or sleeping quarters for two average-sized persons. Below the berth, a fiberglass pan extends to the companionway, incorporating longitudinal stringers that provide support for the berth and separate the space into watertight compartments of 1,800 pounds positive buoyancy. Port and starboard quarterberths are 96″ long, 18″ wide.

A stowage area located below the companionway is large enough for two laundry-sized baskets, one functioning as a low-cost alternative to a spinnaker bag, the other for stowing loose gear. The outboard motor, fuel and dock gear can be stored in a 12″-deep compartment below the cockpit.
From a strictly utilitarian standpoint, most average-sized persons will find the space adequate for overnight camping trips or nights spent aboard during regatta weekends, as long as cooking and bathing facilities are available.
Performance
McWaid, a strapping 150-pounder, managed to have the boat rigged and ready to go sailing within 30 minutes of his arrival at a San Francisco Bay hoist on a blustery March afternoon. Following months of rain, temperatures had risen into the 60’s and winds were blowing 12-20 knots from the west, so we had perfect conditions to test the boat.
Rigging the Ultimate 20 is fairly simple. The mast cradle is elevated at the front of the trailer, which increases leverage during the hoist of the 45-pound mast while it is attached to the trailer winch. After that, preparing to sail is simply a matter of pinning the shrouds to the chainplates; lowering the keel by employing a patented gantry system that controls its passage between Delrin slides built into the hull; securing an aluminum cover to protect the keel from sliding upward while heeled; attaching the tiller; and heading for open water.
Sailing away from the dock, the first impression is of speed and lightness. The boat displaces only 1,100 pounds, 450 of which are in the keel, so it responds to any movement by the crew. Once we sorted out crew positions and settled down, the boat moved forward quickly in only 2-3 knots of wind as we were blanketed by buildings surrounding the marina.
The boat told us very quickly when we’d cleared the seawall and found fresh breezes by burying her shoulder into a 2′ chop, heeling 12-15 degrees, and squirting forward. We found the helm to be well balanced, even in heavy gusts when beating to weather. Clearly, this boat is happiest when it’s away from the parking lot.
Because we sailed without instruments, it was difficult to gauge speed or sail angle, but we felt as though we were sailing high and fast. When the breeze increased, we reduced headsail sag by tensioning a line led through a block on the furler. During tacks, the driver moves across the boat between the end of the tiller and the mainsail sheet while the trimmers duck underneath the boom.
We also noticed during a beat to weather that shorter crewmembers hiked out on the rail couldn’t reach the foot rests built into the cockpit, relying on the 2″ deck overhang for a handhold. The boat is not equipped with lifelines or hiking straps, a drawback. The deck overhang does deflect spray away from the boat, helping to keep the crew dry. Daysailors will find that sailing an asymmetrical spinnaker takes some getting used to, but the ease with which it is launched and the increase in speed justify its growing popularity, especially since it eliminates the need for an acrobat on the foredeck.
Hoisting the chute is a matter of snaking the tack forward to the end of the pole, sweating the halyard, footing off and holding on while the boat builds speed. Depending on sailing conditions, the jib may be furled or flown.
The boat is fairly forgiving but you have to think fast. While attempting to see how close we could sail to the wind, we nearly broached. Canepa yelled, “We’re going over,” eased the sheet as we rounded up, then trimmed the chute as it filled on a downwind course. Total time to crash, burn, and recover was less than 15 seconds. The key to jibing, we learned, is the release of large amounts of sheet before the main comes across; this way the chute fills in front of the headstay before being blanketed by the main.
We spent an hour putting her through her paces before heading back to the marina, during which time we were impressed with both upwind and downwind performance, as well as the degree to which she seems to meet Canepa’s objective of producing a boat that is both fast and friendly.
We’d feel comfortable sailing it in 20-knot winds and steep chop, but would think twice before taking the Ultimate 20 into open seas. Canepa related that he filled one boat with freshwater to test buoyancy and it didn’t sink. It can be fully enclosed with hatch boards, and there’s room for additional buoyancy.
Conclusions
We’d recommend shoppers take a careful look at the boat for several reasons, first of which is that we think it has a legitimate appeal to a vast audience of saltwater and freshwater sailors. The large cockpit, ease of handling, and speed will be appreciated by casual daysailors, so the boat won’t sit ignored in the parking lot. Racers will be able to push it hard while competing in a one-design fleet under strict class rules. It is well-constructed. Accommodations are adequate for overnighting, and it is easily trailerable.
Total weight of boat and trailer is 1,500 pounds, the keel is only 9″ deep when retracted, so it presents a low profile on the road.
Compared to other sprit boats, it is very affordable: Cost of the basic boat is $19,500, with sails adding $2,900, and a trailer $1,800. A 3-hp. Outboard provides plenty of auxiliary power.
Finally, the boat has been well-accepted in the marketplace: 40 boats have been ordered for delivery in the US and Europe since its introduction one year ago, so it appears likely that racing fleets will be developing.











Hello. I recently purchased a sailboat from a private party. He says its a Schock 20, built in 1972. I am trying to find replacement parts since I am restoring this boat. I was told the WD Schock company was sold by Ruth Schock. They (Ruth Schock) currently make power boats. She did give me the number to the people who bought the sailboat company, but I have left 2 messages and nobody returns my call. Can you be of any assistance in trying to figure this all out? I am going to refurbish regardless, but to actually KNOW this boats origin would be very helpful. Thank you for any assistance you can be
John White
(951) 451-0404
Homeland CA
looking for the plexiglass deck cover for the keel when it is in the down position. Any ideas, photos? Thanks David Hills 6036746412