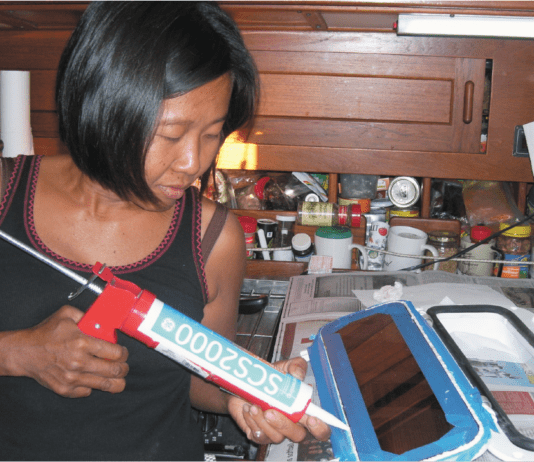
Whey Overdue for a Recoat
Practical Sailor often supplements panel testing with product challenges aboard our test boats to see whether top products still earn their keep in the real world and to try out new products. Two such evaluations are our exterior wood finish tests. In the January 2011 issue, we introduced a head-to-head matchup of varnish alternatives—market-newcomer PolyWhey from Vermont Natural Coatings versus perennial favorite Interlux’s Sikkens Cetol Natural Teak—that had been applied to our Cape Dory 25 test boat. For that test, we’ve just let nature run its course: no band-aid touchups, no maintenance coats, no freshwater rinses, no TLC at all.
Where Credit is Due: August 2011
Letters to Practical Sailor, August 2011. This month's letters cover subjects such as: Weems and Plath, and Moorhouse Sailmakers.
Metal Chafe Plates: Functional Remedy for Scrapes and Scratches
What do you do when the pin in the leg of your folding cabin table digs up the cabin sole? What do you do about the groove in the top of the teak toerail caused by your dock lines? What about the scuffs in the varnished bulkhead behind the companionway ladder? The answer is that you make chafe plates to solve all three problems. While chafe plates can be made out of almost any material — sheet PVC, thin stainless steel, aluminum — the most readily available and easily worked stuff is plain old brass. Brass can be purchased in many forms: sheet, solid round bar, pipe, tubing, and half oval, for example. It is quite cheap. If you have a local scrap metals dealer, you can buy enough scrap brass in various forms for $10 or less to keep you busy with a lifetime of projects. If there's no metal dealer at hand, most hobby shops carry substantial supplies of brass, although hobby shop brass tends to be thinner than what you want for most jobs.
It Takes a Tough Sailor to Make a Smooth Boat Bottom
Fairing in through hull fittings, as described in the February issue, will go a long way toward reducing bottom drag in light air, but it won't really do the job unless the paint surface of the bottom is smooth. A surprisingly high percentage of boats not used primarily for racing have bottom paint jobs that range from poor to atrocious. If your bottom has peeling patches that haven't been in, brush marks from failure to smooth out thick bottom paints, or stipple marks from application with a roller, your boat will be slower in light air than it could be. Bottom paints, unlike topside paints, are not formulated for smooth application, in most cases. They have a high solids content and quick-flashing solvents, a combination guaranteed to make smooth application difficult. Even the racing boat with the smoothest bottom didn't start out that way.
Teak: A Little Effort Goes a Long Way
Probably nothing can make or break the appearance of a fiberglass boat more quickly than the appearance of the exterior teak trim. Contrary to popular belief, teak is not a maintenance-free wood that can be safely ignored and neglected for years at a time. Though teak may not rot, it can check, warp, and look depressingly drab if not properly cared for. Although it is not immune to neglect, teak is incredibly resilient, and can be brought back to life after remarkable amounts of abuse. Therefore, there is no excuse for drab, ugly exterior teak on any boat. Unlike other woods used for exterior trim, the grey weathering of teak rarely extends very far below the surface of the wood.
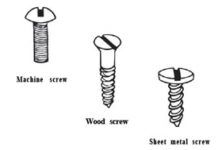
Proper Fastenings: Don’t Screw Up
The ultimate in trivial significance is probably Richard III's lament about losing a battle for lack of a nail. By contrast, use a nail in a fiberglass boat and it's likely the boat will be lost. Nails as well as wood screws have little application on a modern boat. The reason is simple: almost any fastener will do a better job than either. In this day and age the most practical fastener material is stainless…
Lay New Nonskid to Restore Worn Decks
We don't really know what the life expectancy of a fiberglass boat may be. There are lots of them out there that are more than 20 years old, still going strong. We do know, however, that no matter how longlived fiberglass may be as a structural material, over time the gelcoat surface commonly used in finishing fiberglass becomes porous and chalky, and has the unfortunate tendency to crack and craze. Gelcoat, in other words, weathers just as a painted surface will over time. With topsides, a tired gelcoat surface can be restored to better than new condition through the use of polyurethane paints, which can retain color and gloss for years. Decks, however, are another story.
Replacing Teak Decks, the DIY-er’s Way
Practical Sailor contributor and world cruiser Joe Minick details the steps he and his wife took to replace the wornout teak deck aboard their Mason 43, Southern Cross. Minick breaks down the major tasks of the three-month project and explains how they saved a lot of money by doing some of the work themselves. The article looks at the pros and cons of a do-it-yourself teak deck refit; planning and budgeting; step-by-step removal of hardware and the old deck; and the detailed installation process of the new deck.
PS Advisor: Rotten to the Core
Do you have any suggestions on a book or manual that explains how to replace a cored deck where most of it is soaking wet? I replaced a 1.5-square-foot area and was surprised to see that it was so wet and rotten that I could grab the wood core and squeeze it like a sponge.
Laid Teak Decks: Hallmark of Quality
There was a time when laid decks — teak, yellow pine, or fir — were the hallmark of a true yacht. The bare wood gave secure footing, easy maintenance, and reasonable protection from leaks. Since the advent of fiberglass, those same laid decks, almost universally of teak, have continued to represent that hallmark. However, they have become at least as much a cosmetic feature as a functional one. Teak decks, cockpit seats, cockpit sole, hatchtops, and cabin sole all lend themselves to being planked (or sheathed) in a traditional manner Almost no project can do more to "dress up" a boat than some laid decking, and it is a job the average boatowner can do himself. This article describes a simple method for laying decking, one we have used ourselves.