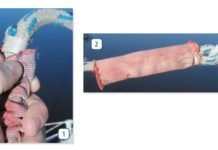
Sewn Splices Two-Year Followup
The true test of marine gear is not whether it works when installed, but rather how it functions after years in the field. To that end, we have left samples of sewing materials and sewn test samples in the sun, wind, rain, and snow for two years, and have also sailed with sewn samples in service on our test boat.
The No-sew Webbing Strap with Link Buckle
Weve sewn our fair share of eyes in nylon webbing, but heres an easy no-sew alternative for creating a webbing strap with a buckle (shackle) that can be used for easily lashing down the dinghy, a battery, or even holding up your pants in a pinch. It is based on stuff a sailor has on hand-webbing, a chain link, and a shackle-and is as strong as professionally sewn ends, plus it can be untied after loading. It has tested at greater than 85-percent breaking strength and 100 percent of minimum rate strength, and it works on both nylon and ultra-high strength materials like Vectran webbing.
Fitting a Roller Furling Line
Replacing the roller-furling control line is an easy do-it-yourself job for the boat owner. Inexpensive, double-braid Dacron is a fine choice for furling lines on most boats shorter than 40 feet. On longer boats, you can opt for a furling-line material of more esoteric double-braids with less stretch. However, any line smaller than 3/8-inch diameter is too difficult to grip.
Testing a Dynamic Traveler
Sailors gaze longingly at the rope wall at the local chandlery, coveting rope made from exotic fibers that promises ultra-low stretch and light weight, perfect for every halyard, sheet, and running-rigging application. But are they really? Certainly, there must be applications where a little stretch is a good thing, perhaps the best thing.
Untangling Furling-line Fairlead Logistics
Headsail furling on sailboats 40 feet and shorter should be able to be accomplished with a hand-over-hand pull on the furling line. If a large genoa is set and the breeze fills in abruptly, it may take a little coaxing with a winch to get things going, but when its a fairly light-wind day and you need to start cranking away on a primary winch to instigate the furl, something is wrong with the system.
Going Soft on Shackles
Fiber shackles have been in use for centuries-the simple knotted toggles provided all manner of service on square-riggers and even older craft. When made correctly with the right material, fiber shackles are strong, can be released without tools, and are jam-proof in the most severe weather. Like cotton sails, this 200-year-old technology has been updated through the use of modern materials.
Abrasion and Break Testing
Testers first task was to determine whether any of these coatings could weaken line in the near term. To do this, we formed 20-inch loops of 1/8-inch polyester braid and nylon braid, coated a 1-inch length of the loop with each of the products, and broke these in our test rig.
Survey: Mainsail Track Hardware
Its been almost 10 years since Practical Sailor weighed in specifically on mainsail track hardware. (See Practical Sailor, Feb. 1, 2005 online) At the time, we offered a summary of the products designed to manage what we termed the three Ss of mainsail handling-setting, shortening, and striking. In that article, we focused on the gear used with full-battened mainsails, which were becoming increasingly popular among a broad spectrum of sailboat owners then.
Top Whipping Twines
The term whipping twine is somewhat misleading, suggesting a single purpose for a product with seemingly endless uses. These are the thin-woven strands that all hand-sewing projects depend upon, and in the process of exploring various stitching projects, weve gone through spools and spools of it.
Higher Loads Call for Careful Installation
Rope clutches are a great innovation that can help sailors better control the lines that lead aft to the cockpit and those that cluster around the mast base. But as with many good things, there is the risk of over-doing the benefit.